Biospective's unique, proprietary, validated tau animal models (AAV-tau mice; tau PFF mice) are optimized for translational neuroscience drug development. These mouse models feature phosphorylated tau aggregates, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration. These mice serves as excellent models of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP), Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD), and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD). As a neuroscience CRO, Biospective provides efficacy, MoA, and target-engagement studies in these tauopathy models.
Biospective specializes in mouse models of tauopathies, with deep expertise in tau pathology. As a global preclinical contract research organization, we support biotech and pharmaceutical drug development programs using validated tau rodent models for therapeutic efficacy, biodistribution, mechanism-of-action, target engagement, and PK/PD studies across small molecules, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), gene therapy (AAVs), antibodies, and other biologics.
Biospective has developed unique tau mouse models that recapitulate key features of human Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP), Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD), and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD), including misfolded protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, motor dysfunction, and cognitive impairment. Studies include translational biomarkers such as MRI and PET imaging, fluid biomarkers including neurofilament light chain (NfL) & cytokines, and quantitative IHC/IF. With fully integrated, end-to-end preclinical services, Biospective's services enable translational tauopathy research from study design through data interpretation.
Tau Mouse Models – Our Core Expertise
Biospective specializes in disease-relevant tau mouse models for drug development.
Tau protein aggregation and propagation are central to the pathophysiology of numerous neurodegenerative diseases. As part of our neurodegeneration models portfolio, Biospective has built specialized capabilities around tau animal models.
Our first of its kind AAV-tau model recapitulates key aspects of tauopathies with Parkinsonian features, including Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) and Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD). This mouse model expresses human wild-type 2N4R tau in disease-specific brain regions and is a core differentiator of our preclinical CRO services. This model recapitulates key features of human PSP & CBD – including phosphorylated tau aggregates, neuroinflammation, dopaminergic cell loss, and motor impairment. Complementing this AAV-tau model, our tau PFF mouse models serve as excellent models of tau seeding and spreading. Our in vivo services are focused on reproducibility, well-defined model phenotypes, and the integration of cognitive, motor, imaging, biochemical, molecular, and quantitative histopathological endpoints to enable comprehensive in vivo tauopathy efficacy studies and exploration of mechanism-of-action.
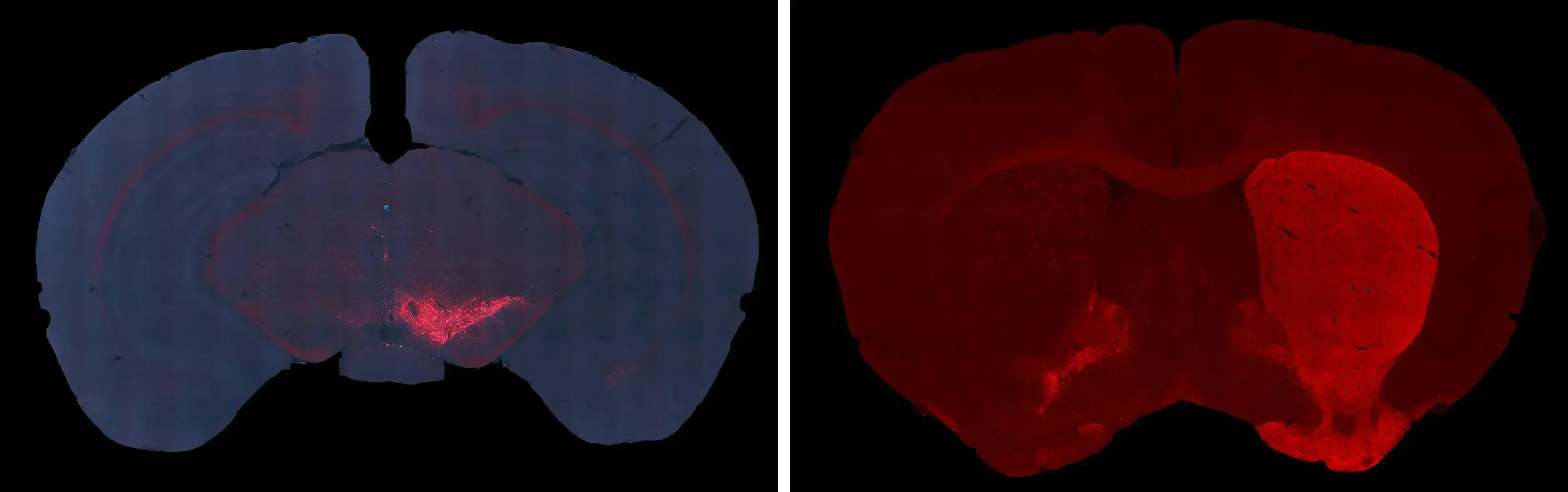
Severe dopaminergic neuron loss and dopaminergic denervation in the ipsilateral (left hemisphere) SNc and caudate-putamen following unilateral AAV-tau injection into the SNc of a C57BL/6 mouse.
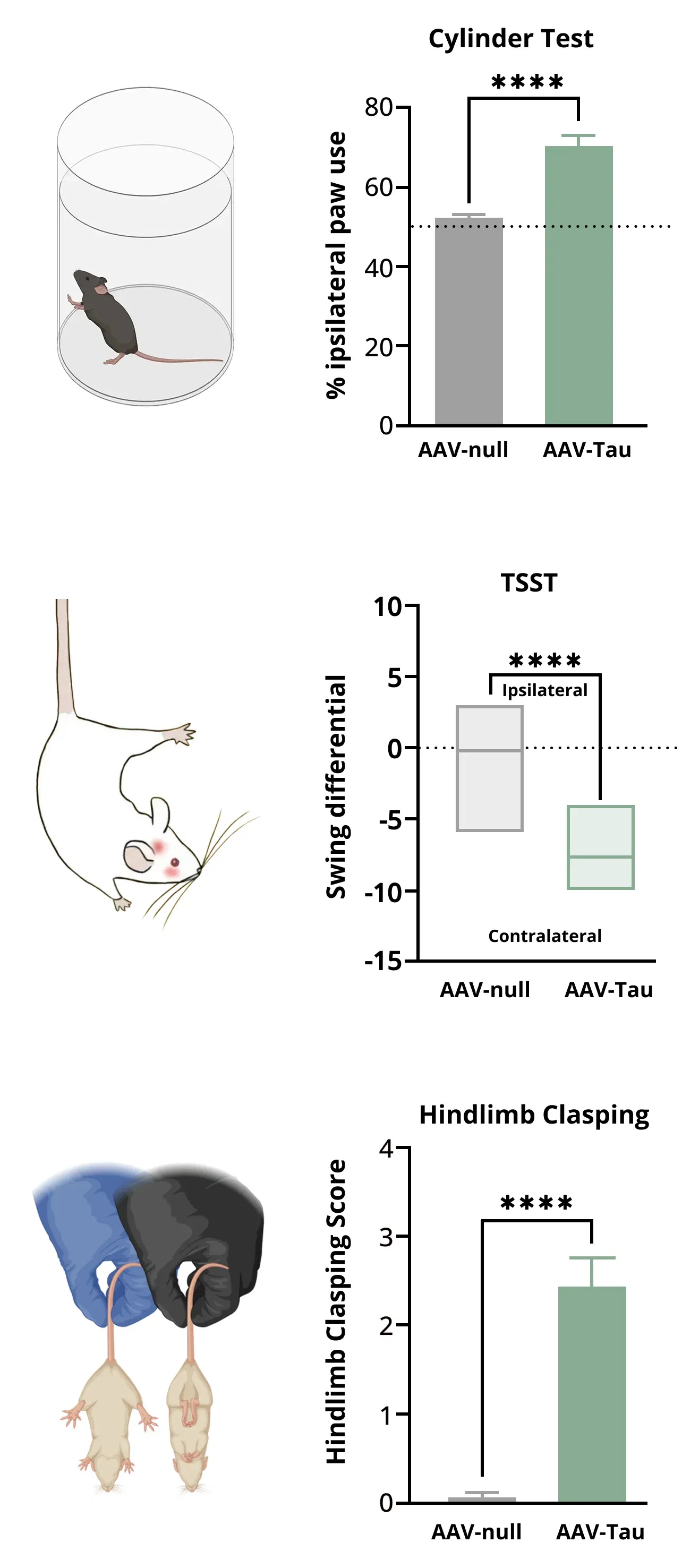
Loss of dopaminergic innervation corresponds with unilateral motor deficits, including increased ipsilateral paw use (Cylinder Test), increased contralateral swings (Tail Suspension Swing Test), and increased hindlimb clasping.
AAV-Tau (2N4R) Mouse Models
Generation of tau pathology in the adult rodent brain can also be achieved via injection of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors encoding tau. In this tauopathy mouse model, adult wild-type (C57BL/6) mice (or suitable genetic backgrounds) receive a unilateral stereotaxic injection of an AAV vector overexpressing human wild-type (2N4R) tau directly into the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc). Our skilled surgical team uses high-precision digital stereotaxic devices with automated microinjectors for accurate viral delivery to the target region. This model replicates dopaminergic neuron loss and other hallmark phenotypes of tauopathies with Parkinsonian features (PSP & CBD), measurable via translational biomarkers, making it unique for drug evaluation.
AAV-Tau Model Induction:
- Unilateral or bilateral stereotaxic injections of AAV expressing human wild-type tau
Validated Injection Site:
- Substantia Nigra pars compacta (SNc) – to induce nigrostriatal degeneration
Disease Features Modeled:
- Dopaminergic neuron loss in the SNc and striatum
- Phosphorylated tau aggregates in the SNc and striatum
- Neuroinflammation (local microglial and astrocyte activation)
- Neurodegeneration (progressive loss of nigral neurons)
- Unilateral motor deficits observable via behavioral tests, including the Cylinder Test, Tail Suspension Swing Test (TSST), Hindlimb Clasping Test, Rotarod Test.
In addition to standard endpoints, Biospective can perform non-invasive imaging studies on AAV-Tau mice – such as MRI volumetric analysis and PET imaging (e.g. [18F]FDG PET for glucose metabolism, [18F]DOPA PET for dopaminergic function) – to generate clinically translational imaging biomarkers (e.g. regional brain atrophy, cerebral hypometabolism, striatal dopamine terminal loss). This AAV-Tau model is also excellent for high-throughput studies (including screening studies) of disease-modifying therapeutics, thanks to its rapid start-up (no breeding needed), use of wild-type animals, cost-effective induction, and suitability for large cohort studies.
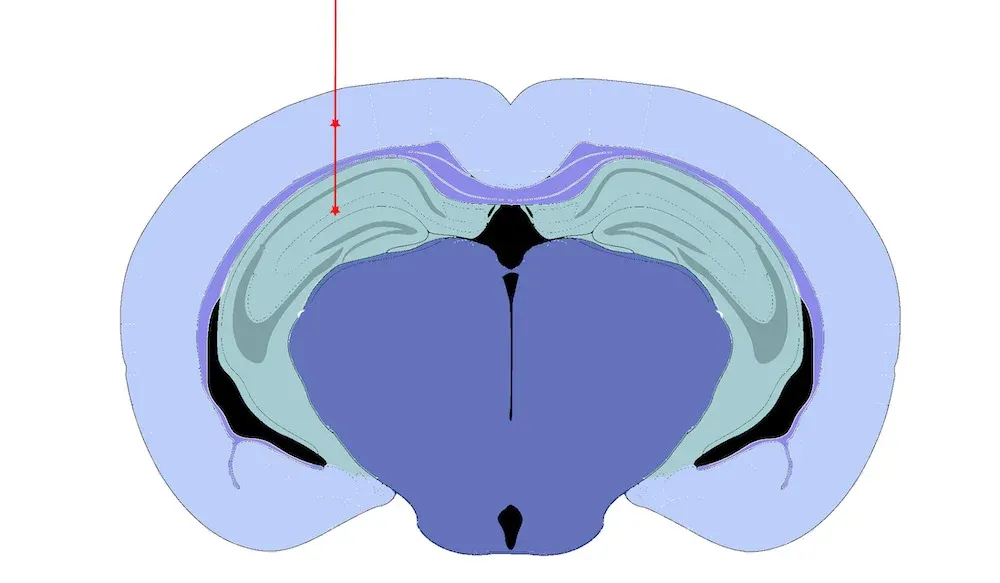
Hippocampus and overlying Cortex Injection Site.
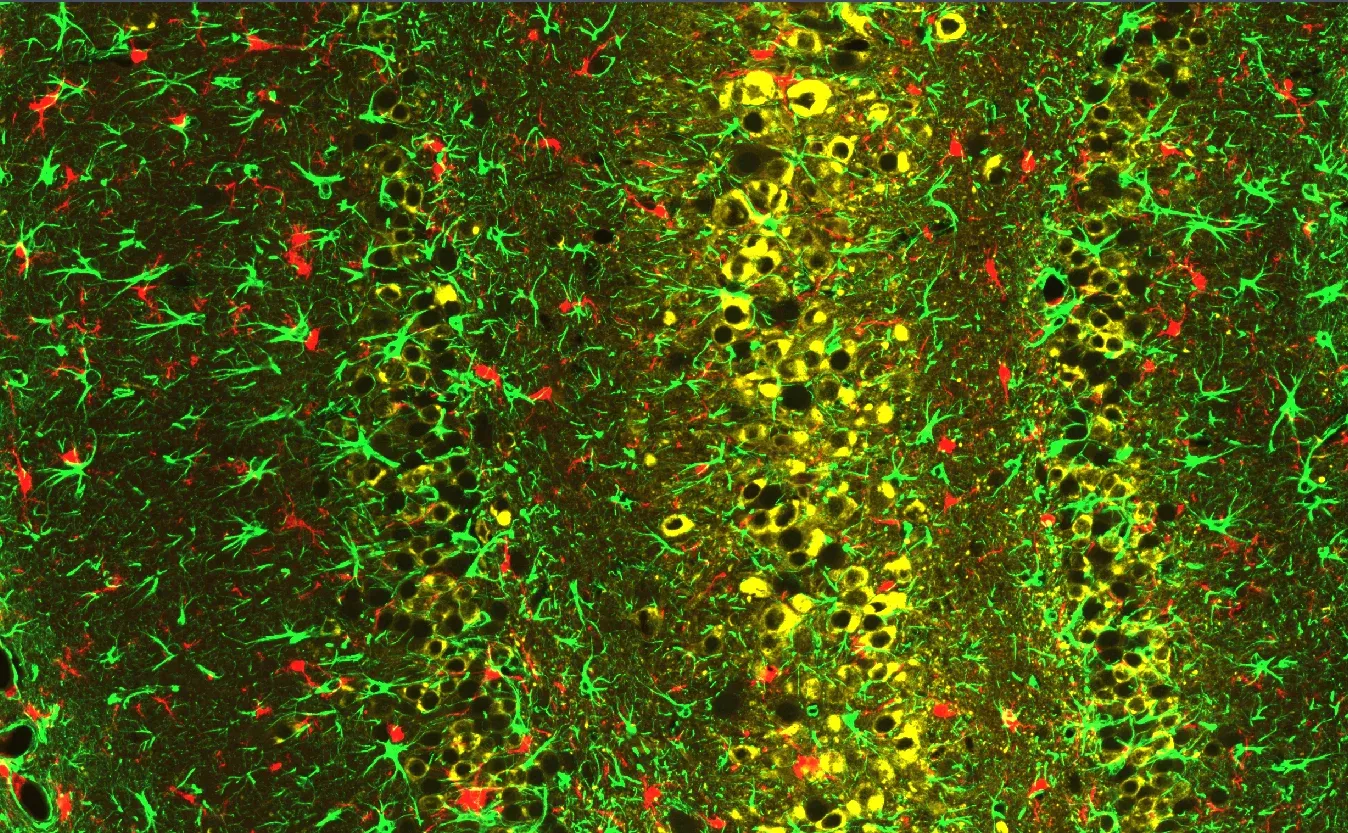
Multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) image showing phoshorylated tau (AT8, in yellow), microglia (Iba-1, in red), and astrocytes (GFAP, in green) in the hippocampus of PS19 mice injected with Tau-PFFs.
Tau Preformed Fibril (PFF) Mouse Model
The pathologic spread of misfolded tau that characterizes multiple neurodegenerative diseases can be recapitulated in rodent brains by stereotaxic injection of tau preformed fibrils (PFFs). In this PFF seeding and spreading model, exogenous recombinant tau fibrils seed the aggregation of endogenous tau and propagate pathology across the brain. This model is induced in transgenic mice overexpressing human tau (e.g. PS19 mice with the P301S mutation).
Tau PFF Model Induction:
- Injection of recombinant tau preformed fibrils
- Applicable to P301S transgenic mice (PS19 line)
Validated PFF Injection Site:
- Hippocampus (± overlying cortex)
Key Disease Features Modeled:
- Progressive spreading of tau pathology in a well-defined spatiotemporal pattern
- Neuroinflammation (microglial and astroglial activation)
Our tau PFF-induced mouse models are highly reproducible and are well-suited for testing disease-modifying therapeutics. The PFF mouse model is commonly used to evaluate therapies targeting tau aggregation and propagation. Biospective has strong experience executing preclinical studies with tau PFF models to evaluate target engagement, mechanism of action, and therapeutic efficacy.
Translational Pathology and Biomarkers in Tau Models
Biospective has established a broad range of clinically-relevant disease markers to facilitate translation to clinical studies.
As a Preclinical Neuroscience CRO, we design our tau models with translational relevance to mirror key aspects of the human disease. A major differentiator of Biospective is our focus on translational biomarkers that align preclinical findings with clinical outcomes – including advanced neuroimaging and fluid biomarkers. We incorporate:
-
Tau–related biomarkers (pathology and spread)
-
Neuroinflammation markers (microglia & astrocyte activation)
-
Neurodegeneration endpoints (neuron loss, brain atrophy)
-
Mechanism-of-action confirmation (target/pathway engagement)
Our modeling and biomarker strategies ensure that preclinical successes meaningfully predict clinical potential, thereby de-risking the transition from animal studies to human trials.
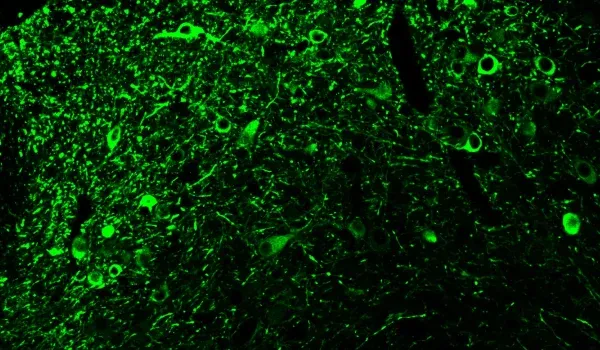
Phosphorylated tau stained with AT8 in our AAV-hTau mouse model.
Tau Pathology
In addition to amyloid-β, tau is a key misfolded protein found in Alzheimer's disease. Tau is thought to be the primary driver of some of the clinical and neuroimaging features of AD (Lew, 2021; Carbonell, 2025). Our APP/PS1/human Tau "co-pathology" model demonstrates both amyloid-β and tau pathology. Phosphorylated tau staining (with various phosphorylation sites) is observed in both cell bodies and processes.
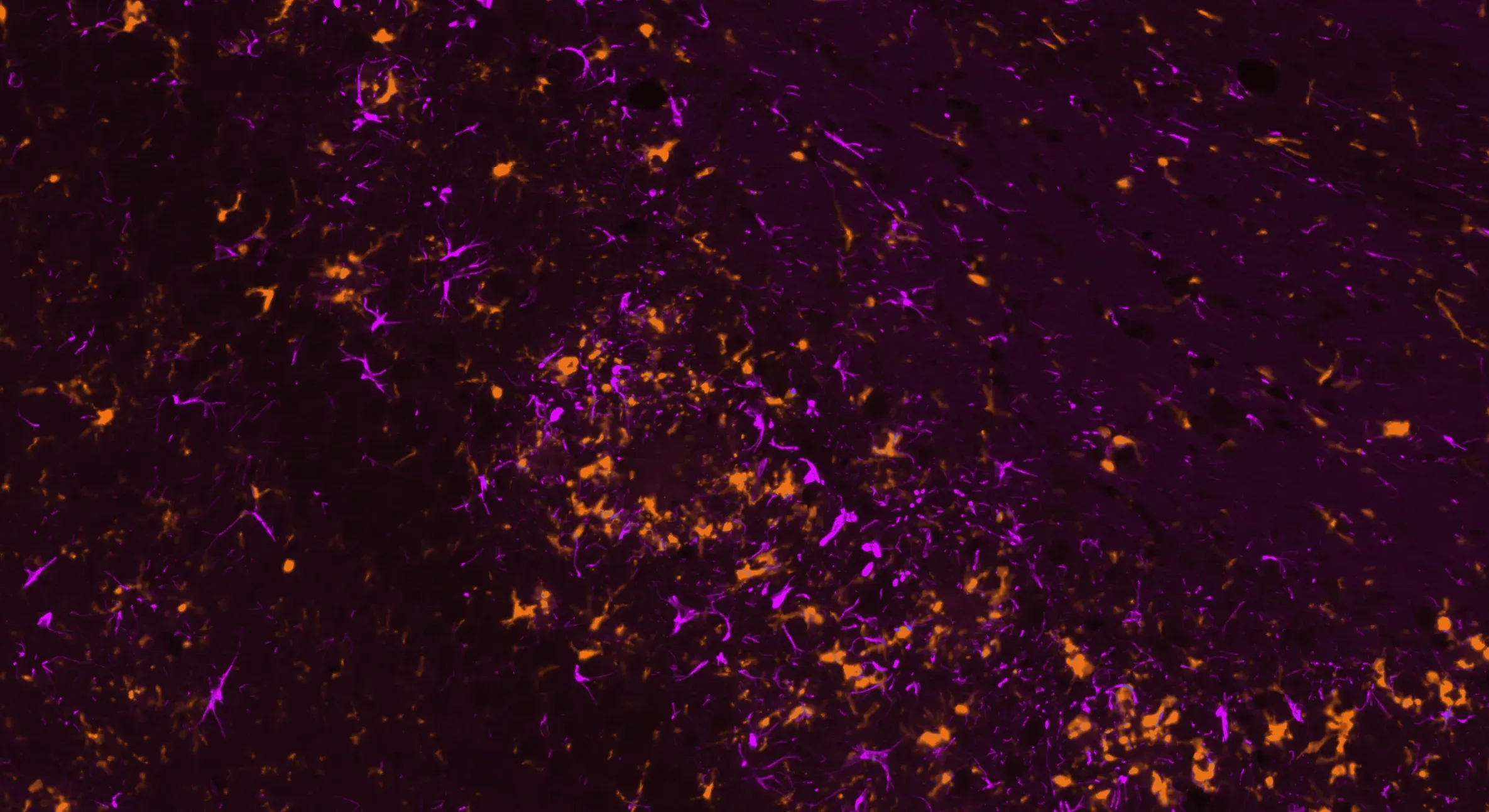
Microglia (Iba-1, orange) and astrocytes (GFAP, violet) demonstrating neuroinflammation in our hTau mouse model.
Activated Microglia & Reactive Astrocytes
Neuroinflammatory cells, including activated microglia and reactive astrocytes, are found in close proximity to misfolded tau in tau-related diseases (Chen and Yu, 2023). We observe microgliosis and astrogliosis in relation to phosphorylated and cleaved tau in our AAV-hTau and Tau PFF mouse models. Learn more from our Initiative - Microglia, Astrocytes, and Neurodegenerative Diseases.
The Tail Suspension Swing Test (TSST) is used to measure unilateral dopaminergic deficits in our AAV-Tau mouse model of PSP / CBD.
Tauopathy Driven Parkinsonian Motor Features
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Degeneration are pure tauopathies which, amongst other clinical manifestations, are characterized by Parkinsonian features and severe loss of neurons in the substantia nigra (Oyangi, 2001). In our AAV-hTau model, we have found significant motor deficits (based on the Cylinder Test, Tail Suspension Swing Test, Rotarod Test, and Hindlimb Clasping Test) as a result of degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and corresponding denervation of the striatum.
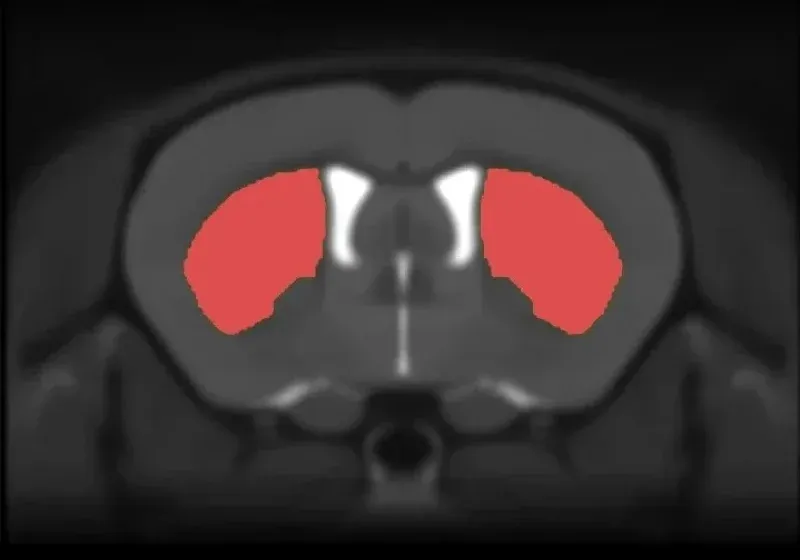
Anatomical MRI of mouse brain showing segmented caudate-putamen for measurement of regional volumes.
Regional Brain Atrophy
Multi-modality imaging biomarkers are widely used in clinical trials of tauopathies. MRI-derived regional volume and cortical thickness measures are highly sensitive to brain atrophy and allow for monitoring disease progression over time in PSP, CBD, and FTD. Using non-invasive, in vivo whole brain MRI acquisition combined with advanced, fully-automated image processing & analysis, we have shown highly significant regional brain atrophy, specifically related to tau pathology, thereby serving as a robust in-life measure of neurodegeneration and a translational biomarker.
Why Choose Biospective as Your Tau Models CRO?
Biospective is a neuroscience CRO with a focus on tauopathy animal models, strong scientific expertise, and extensive experience conducting preclinical studies with Tau models.
-
Specialized Tauopathies CRO: Focused on tauopathies and neurodegenerative disease models, not a generalist animal provider.
-
Multiple Validated Tau Models: AAV and PFF induced tau mouse models are readily available for studies.
-
Tau Expertise: Deep scientific expertise in tau biology and pathology, the central misfolded protein in multiple neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Integrated Services: Fully integrated preclinical services from study design to data interpretation, ensuring seamless execution.
-
Proven Efficacy Data: Industry-standard tau models efficacy datasets and extensive historical controls for robust benchmarking.
-
Accelerated Timelines: Rapid study initiation and efficient workflows to compress timelines without sacrificing quality.
-
Translational Biomarkers: Advanced biomarkers (MRI, PET imaging, CSF/blood assays) that bridge preclinical findings to clinical outcomes.
- Flexible & Customized Study Designs: Our scientists work with your team to customize the study design to best fit your goals.
-
Global Support: Experience supporting biotech and pharma clients worldwide, with responsive project management and communication.
Our scientists work as an extension of your internal team, collaborating closely to ensure scientific rigor, reproducibility, and translational relevance at every stage of your tau research program.
End-to-End Tau Models Preclinical CRO Services
Biospective offers fully integrated preclinical contract research services.
-
Study design & model selection – expert guidance on choosing the right tau model and designing robust studies
-
In vivo efficacy studies – execution of treatment studies with comprehensive monitoring of outcomes
-
Biodistribution & PK/PD – analysis of drug distribution and pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics in CNS and periphery
-
Target engagement assays – confirmation that the therapeutic hits its molecular target (e.g. tau reduction, pathway modulation)
-
Behavioral analysis – cognitive testing (Novel Object Recognition, Y-maze, etc.) and motor function testing (hindlimb clasping, cylinder test, tail suspension swing test, rotarod, etc.)
-
In vivo multi-modality imaging – MRI, PET, SPECT, fluorescence, and bioluminescence imaging to track disease and treatment effects
-
Immunoassays – biomarker quantification in CSF, blood, and tissue (e.g. NfL, cytokines, chemokines)
-
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) & multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) – post-mortem tissue staining & quantitative image analysis to assess pathology and therapeutic impact
-
Data analysis & reporting – rigorous quantitative analysis, statistics, and comprehensive reporting by our scientists
This end-to-end approach minimizes handoffs, accelerates timelines, and reduces risk for our sponsors by keeping all aspects of the study with one expert team.
How are Tau Mouse Models Used in Drug Development?
We work closely with our biotech and pharma sponsors to:
-
Evaluate therapeutic efficacy and dose-response in tau models
-
Assess target engagement and disease-modifying effects
-
Support translational biomarker strategies, including imaging and fluid biomarkers for clinical readiness
Our tau mouse models are optimized for in vivo testing of multiple therapeutic modalities, including both traditional and advanced approaches:
Small Molecules
-
Brain penetration and PK/PD profile
-
Behavioral efficacy on cognitive symptoms
-
Reduction of pathology (tau aggregates, neuron loss)
RNA-Targeted Therapies
- Target knockdown verification (e.g. mRNA or protein level reduction)
-
CNS biodistribution of ASOs/siRNA
-
Translational biomarker readouts to confirm pathway engagement
Gene Therapy & Viral Vectors
-
Transgene expression levels in target regions
-
Regional biodistribution of viral vectors (e.g. AAV spread)
-
Functional rescue or disease modification outcomes (behavioral and pathological improvements)
Antibodies & Biologics
-
CNS exposure and penetration of biologics (e.g. BBB engagement)
-
Aβ and Tau aggregation clearance or reduction
-
Mechanism-of-action validation (target binding, downstream signaling changes)
Learn more about our in-depth characterization of these Tau mouse models, our validated outcome measures, and the full scope of our Tauopathies CRO services.
Related Content
Up-to-date information on Tau and best practices related to the evaluation of therapeutic agents in Tau animal models.
PS19 Mouse Model for Tau Targeted Drug Development
An overview of PS19 (P301S) mice as a transgenic model for preclinical evaluation of disease-modifying therapies targeting tau seeding & spreading.
A Guide to Mouse Models of Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
A Resource providing a comprehensive overview of animal models used in frontotemporal dementia research, including genetic and pathological disease mechanisms.
Microglia, Astrocytes & Tau in Neurodegenerative Diseases
How glial-driven neuroinflammation fuels tau aggregation, propagation, and neuronal loss in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies.
NLRP3 Inflammasome and Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of the NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson’s disease, and ALS.
Autophagy & Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of how cellular autophagy plays a role in brain health and neurodegeneration.
Impaired Microglia Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases
How impaired microglia autophagy contributes to the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Interleukin-1 Beta (IL-1β) and Neurodegenerative Diseases
The role of IL-1beta in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Lysosome Dysfunction in Microglia & Astrocytes
An overview of lysosomal dysfunction in microglia & astrocytes, and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.
Microglial Senescence and Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of microglial senescence and its role in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Microglia & Astrocytes
The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in microglia and astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and ALS.
TNF-α (TNF-alpha) & Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of the function of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in microglia and its contribution to the progression of neurodegeneration.
Inflammasome – A Therapeutic Target for Multiple Diseases
An overview of inflammasomes, including their mechanisms of action, roles in diseases, and targeting for drug development.
Microglia-Neuron Interactions & Neurodegenerative Diseases
A concise review of the direct interactions between microglia & neurons, and how these cell-to-cell interactions may be affected in neurodegenerative diseases.
TNF-α & (TNF-alpha) Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of TNF-α signaling in astrocytes, its role in neurodegeneration, and therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway..
What is Pyroptosis? | A Drug Development Perspective
An overview of pyroptosis, its role in various diseases, and therapeutic strategies related to pyroptosis pathways.