Microglia-Neuron Interactions in the Alpha-Synuclein PFF Mouse Model
Biospective’s alpha-synuclein PFF mouse models accelerate Parkinson’s disease drug development with translational synucleinopathy for preclinical research. As a global neuroscience CRO with deep expertise in synuclein PFFs injection into transgenic A53T (SNCA) mice, we offer end-to-end in vivo services — including efficacy, PK/PD, mechanism-of-action, and target engagement — backed by advanced imaging, quantitative IHC, and biomarkers.
At Biospective, our alpha-synuclein preformed fibril (PFF) mouse models are purpose-built to advance Parkinson’s disease preclinical programs with translational relevance. With unmatched experience in PFF injection into A53T (SNCA) transgenic (M83) mice to induce seeding & spreading of α-synuclein pathology, we provide comprehensive in vivo services — including efficacy testing, biodistribution, mechanism-of-action studies, PK/PD, and target engagement — supported by an in-house colony of A53T mice, behavioral assays, MRI/PET/SPECT, quantitative IHC, multiplex immunofluorescence, and translational biomarkers, such as neurofilament light chain (NfL) and cytokines, to generate decision-ready data for biotech and pharmaceutical partners worldwide.
Overview of the Alpha-Synuclein PFF Parkinson’s Model
A disease-relevant synuclein Parkinson's mouse model for preclinical drug development.
Biological Rationale and Disease Relevance
Alpha-synuclein (α-syn) aggregation and spread are central drivers of Parkinson’s disease pathology. In Biospective’s α-synuclein PFF mouse models, Parkinson’s-like synucleinopathy is induced by stereotaxic injection of recombinant α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse brain. These fibrils seed endogenous α-syn misfolding and propagate through anatomically connected regions, recapitulating key features of human Parkinson’s disease, including Lewy body–like pathology, neuroinflammation, and progressive neurodegeneration.
Transgenic and Wild-Type PFF Model Options
At Biospective, we perform injections into the brains of:
-
A53T SNCA transgenic mice (M83 line) overexpressing human mutant α-synuclein using human PFFs
-
Wild-type mouse PFF models using murine α-synuclein fibrils
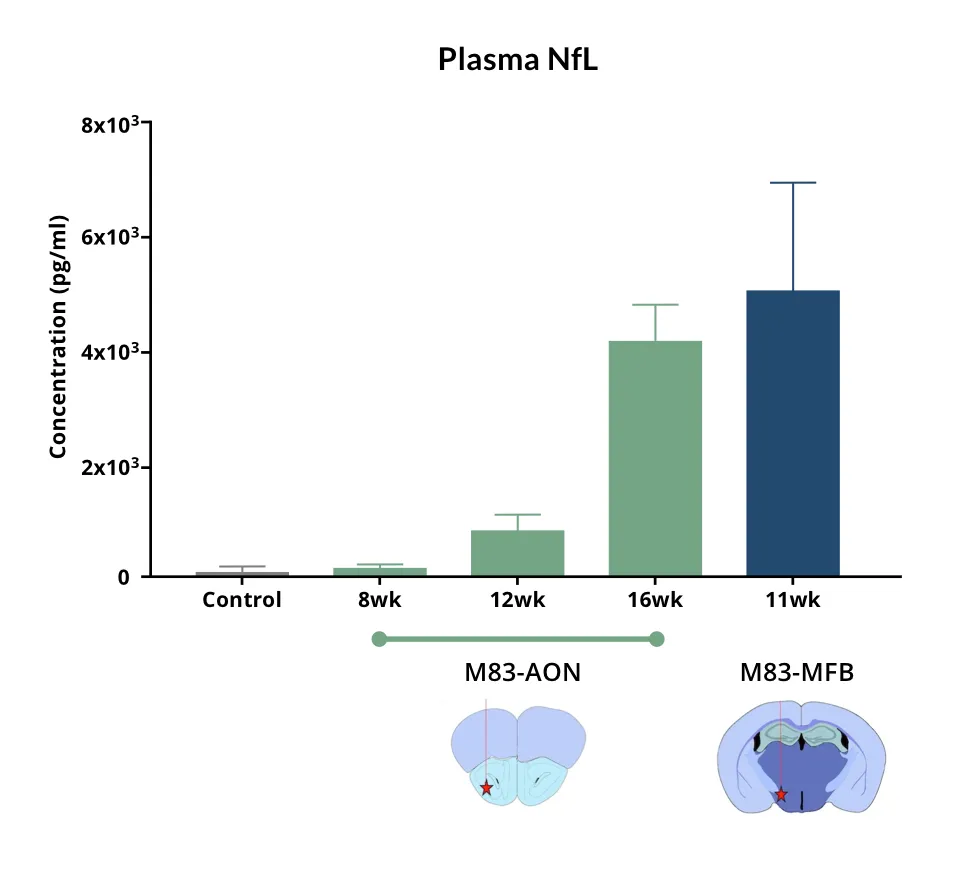
The A53T transgenic PFF model develops faster, more severe, and more widespread pathology than wild-type mice, enabling robust detection of neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, biomarker changes (e.g. elevated NfL in plasma & CSF, MRI-detectable brain atrophy), and functional impairments (sleep-wake cycle alterations, motor deficits) that are not observed in milder wild-type models. As such, the A53T PFF model is particularly well suited for preclinical therapeutic efficacy and target engagement studies.
Animation of unilateral stereotaxic injection of α-syn PFFs resulting in seeding and spreading of pathology.
Validated PFF Injection Sites and Disease Induction
Our validated stereotaxic PFF injection sites include:
-
Anterior Olfactory Nucleus (AON) – modeling early Braak-stage pathology and widespread limbic/cortical spread
-
Striatum ± Cortex – engaging the nigrostriatal pathway
- Medial Forebrain Bundle (MFB) – targeting dopaminergic neurons with induction of motor deficits
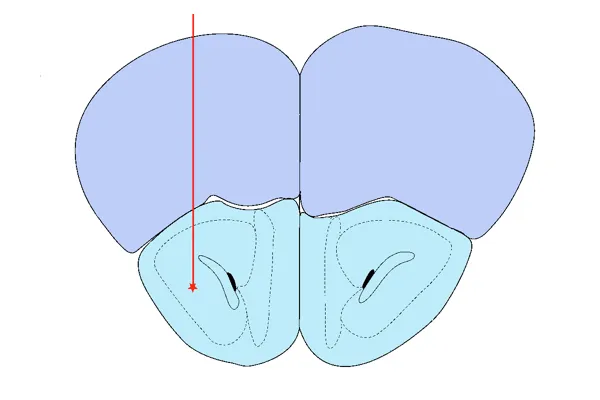
AON Injection
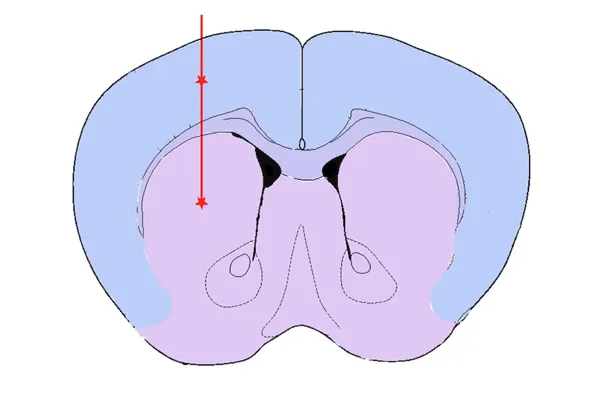
Striatum & Overlying Cortex Injection
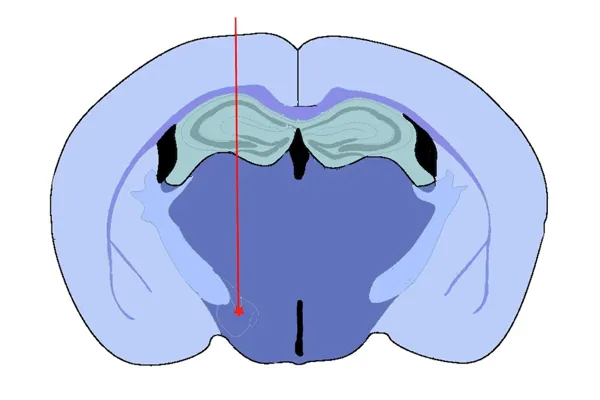
Medial Forebrain Bundle (MFB) Injection
All injections are performed by our expert team using digital stereotaxic systems with automated microinjectors for highly accurate and precise delivery of sonicated PFFs to the target region. A distinct advantage of the PFF model is acceleration of pathology compared to conventional transgenic models. We typically perform PFF injections into 8 week-old mice, thereby dramatically reducing study timelines.
Spatial pattern of spread of α-synuclein pathology following unilateral stereotaxic injection of recombinant preformed fibrils (PFFs) into the anterior olfactory nucleus (AON).
Injections into the mouse brain can be performed unilaterally or bilaterally. Unilateral injections allow for assessment of the spread of synuclein pathology to the contralateral hemisphere, which can be advantageous for evaluating the slowing or halting of spreading. Bilateral injections result in a higher level of a pathology that is also relatively symmetric between the left and right hemispheres, allowing one hemisphere to be fixed for histopathology while the other hemisphere can be snap frozen for biochemical & molecular studies and/or drug exposure analysis.
Key Disease Features and Redouts of the α-Syn PFF Model
Biospective’s α-synuclein PFF mouse models faithfully recapitulate many hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease with clinically aligned endpoints for efficacy, target engagement, and decision-making.
Notable translational features observed in this model include:
-
Misfolded α-synuclein aggregation and spread: Abundant phosphorylated α-synuclein inclusions (Lewy body–like aggregates) develop and propagate in a stereotyped spatiotemporal pattern throughout connected brain regions. Pathology initiated at a focal injection site gradually appears in downstream areas (reflecting the prion-like spread of α-syn). The induction of pathology is highly penetrant (~100% of PFF-injected mice) and reproducible in its distribution.
-
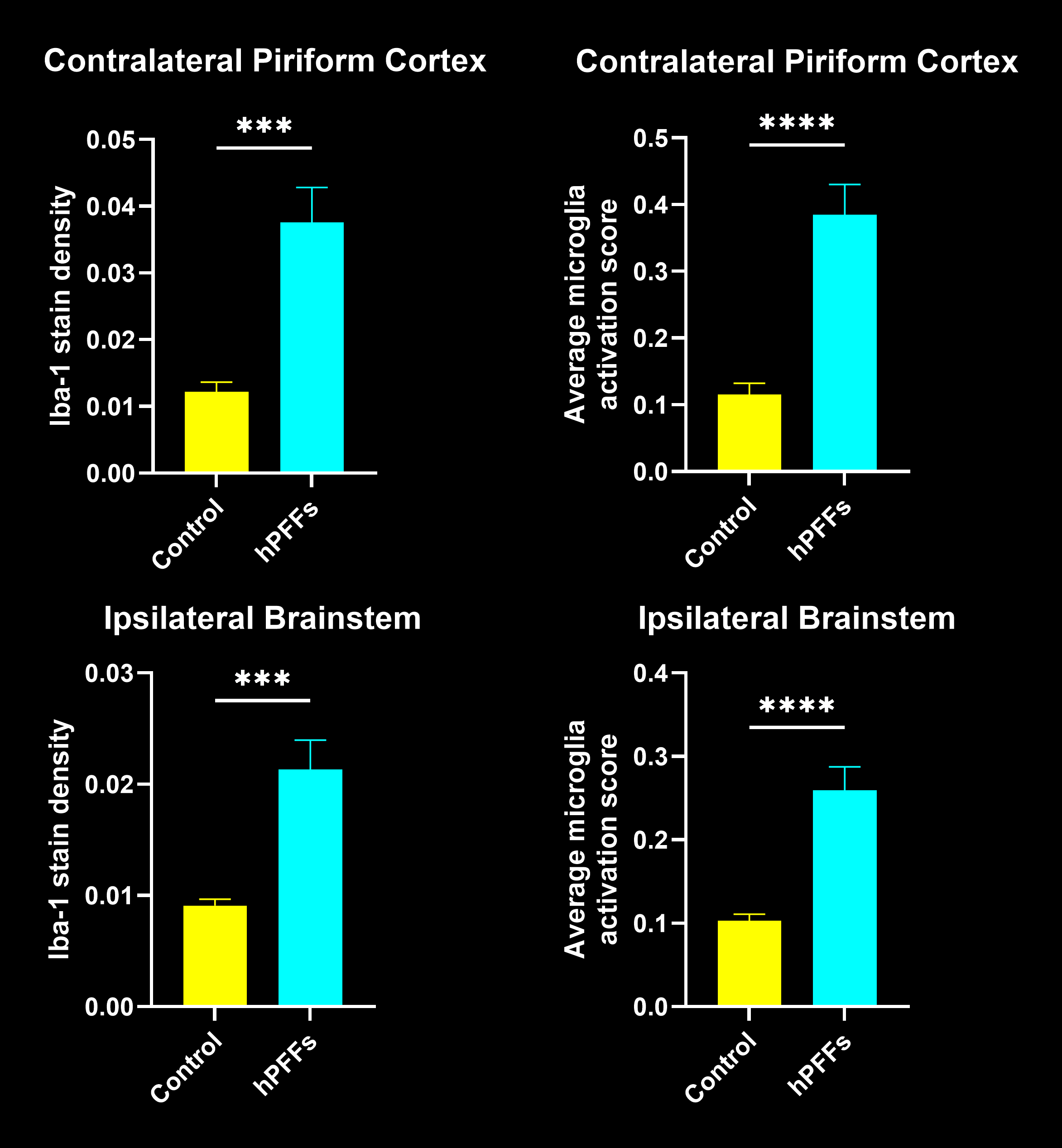
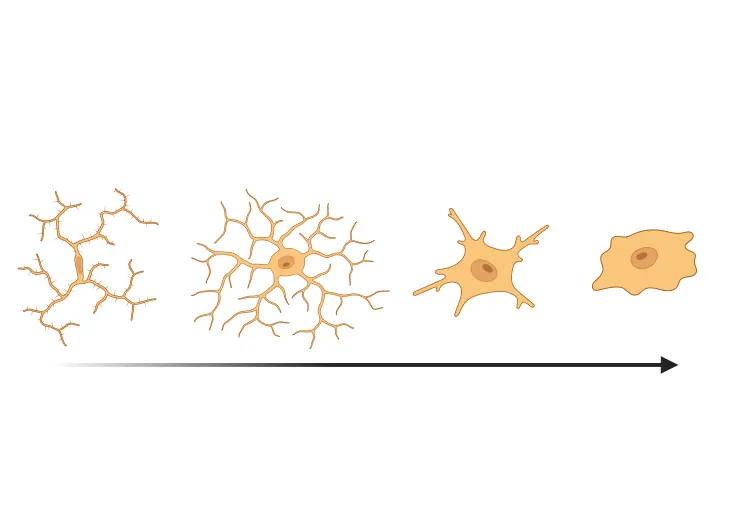
Robust Neuroinflammation: The model elicits a strong microglial and astroglial activation response in regions accumulating α-syn aggregates. This neuroinflammation (microgliosis, astrogliosis) parallels that seen in PD brains, providing an opportunity to evaluate anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory interventions. (See our Presentation: Microglial Activation in an α-Synuclein Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease)
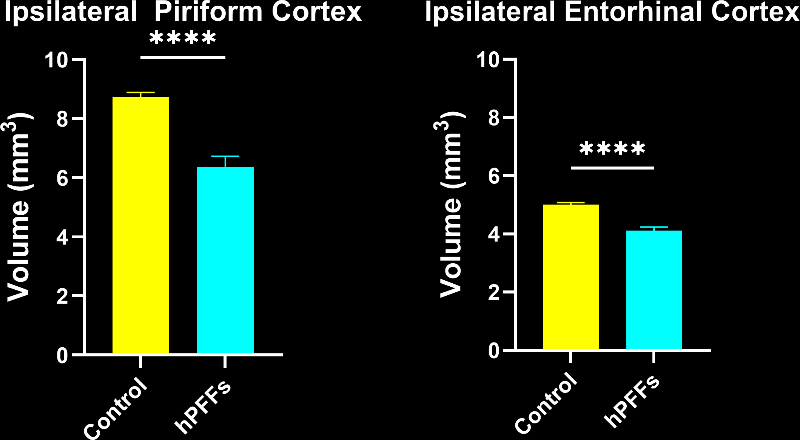
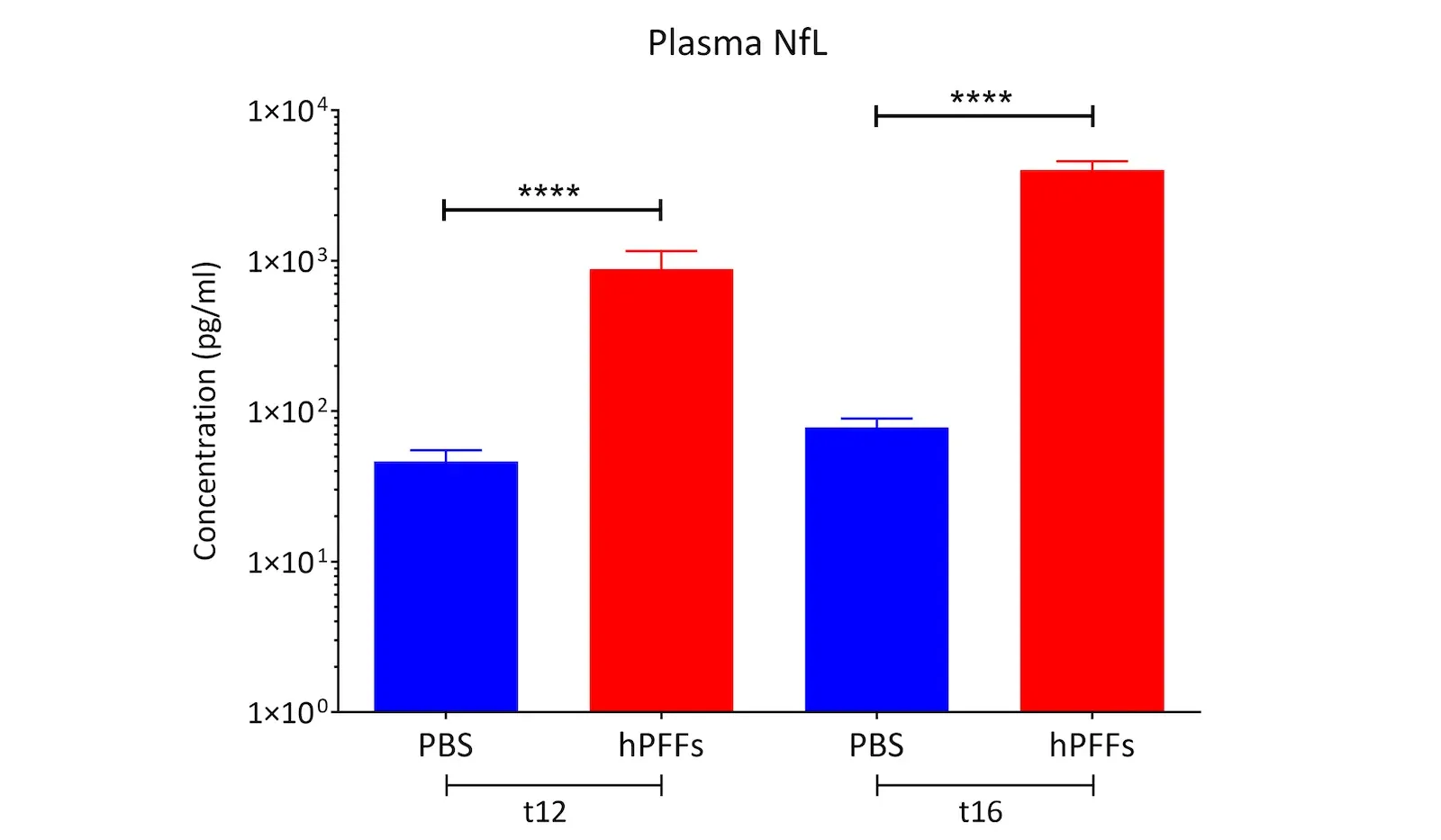
- Neurodegeneration: Progressive loss of neurons throughout the brain is a defining outcome. This neurodegeneration is accompanied by surrogate biomarkers of neuronal loss – for example, we observe significantly elevated neurofilament light (NfL) levels in the blood and CSF of PFF-seeded mice. We also measure brain atrophy on MRI in affected regions as the pathology progresses, mirroring the structural degeneration in PD patients. (See our Presentation: Brain Atrophy Analysis in Mouse Models of Neurodegeneration and our Resource: Neurofilament Light in Parkinson's Disease Models.) These translational markers can be monitored longitudinally, thereby providing the ability to track disease progression to mimic clinical trial conditions.
-
Dopaminergic Neuron Pathology: Synuclein pathology in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) with accompanying motor deficits observed in the MFB injection model.
-
Behavioral and Motor Impairments: The widespread synuclein pathology and nigrostriatal pathology translate into measurable behavioral deficits. PFF mice develop motor impairments. They also exhibit non-motor symptoms such as changes in sleep architecture (sleep disturbances) and olfactory impairments, reflecting the limbic and olfactory network involvement. A battery of behavioral tests (e.g. hindlimb clasping, sleep monitoring, etc.) is used to quantify these functional outcomes.
-
Amenability to Therapeutic Intervention: A key advantage of this model is that it can be modified by treatments. Disease-modifying therapeutics targeting α-synuclein aggregation or related pathways have shown efficacy in PFF model studies. For instance, treatment with an α-synuclein-targeted antibody (ABBV-0805) was shown to reduce pathological α-syn accumulation and extend survival in PFF-injected transgenic mice. This study demonstrates that the model is suitable for evaluating therapeutic efficacy and target engagement – successful interventions can produce measurable improvements in pathology and function in these animals.
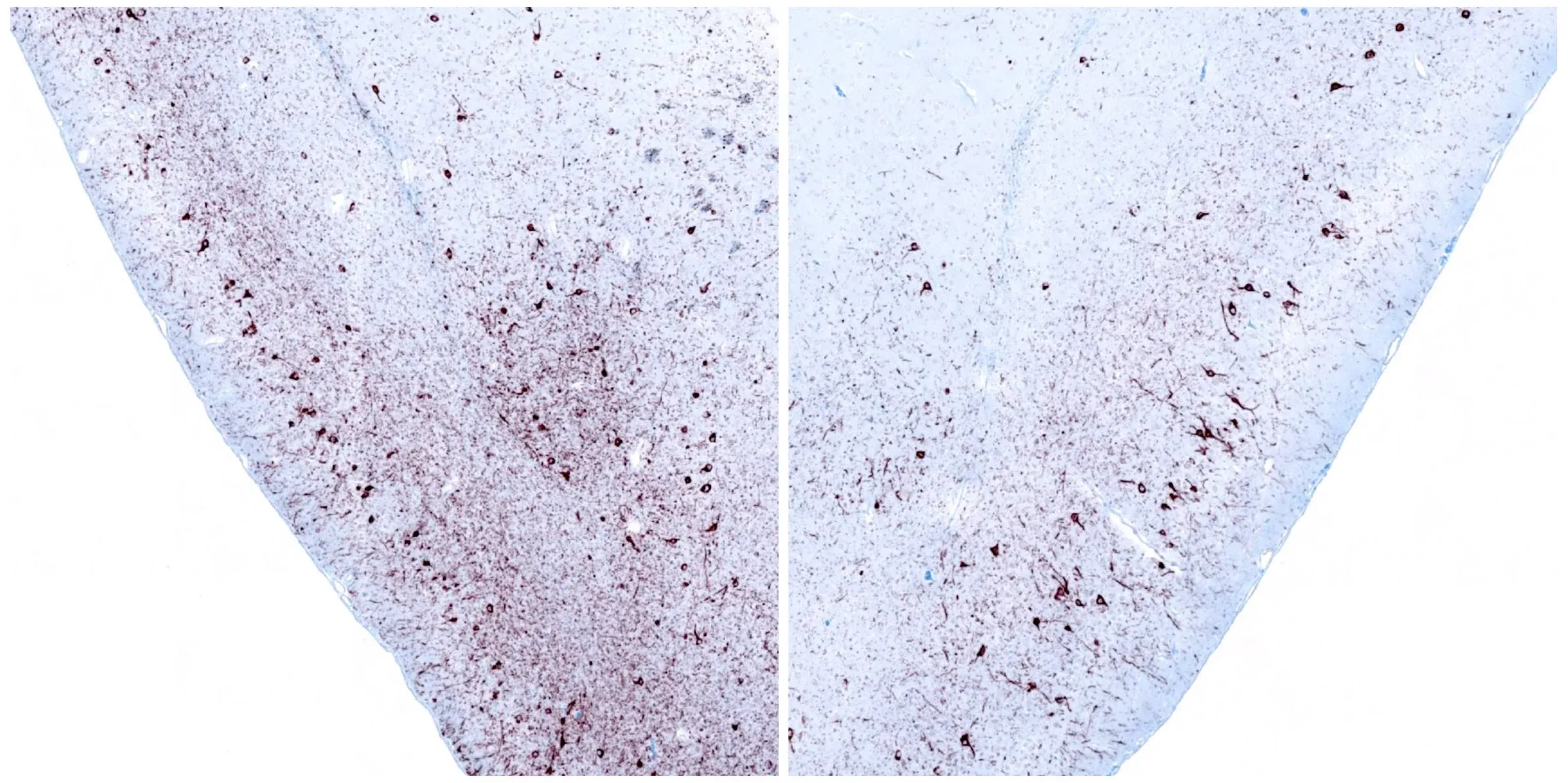
Phosphorylated α-synuclein immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of the ipsilateral (left) and contralateral (right) piriform cortex at 12 weeks following unilateral stereotaxic injection of α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the anterior olfactory nucleus of an M83+/- mouse.
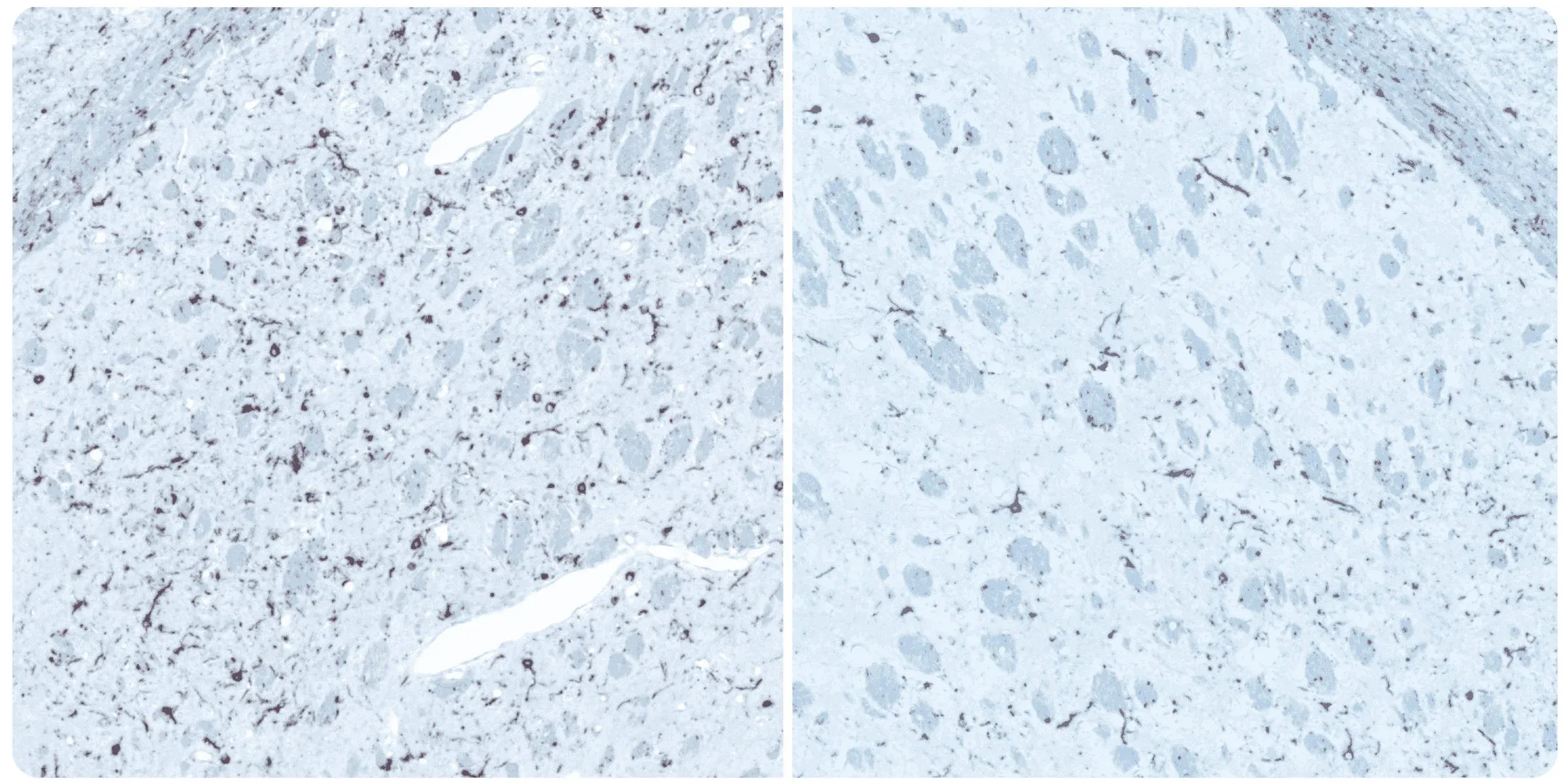
Phosphorylated alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of the ipsilateral (left) and contralateral (right) striatum at 12 weeks post-injection following unilateral stereotaxic inoculation of α-synuclein preformed fibrils (PFFs) into the striatum and overlying cerebral cortex of an M83+/- mouse.
Research Study — Microglia-Neuron Interactions in Alpha-Synuclein PFF Mice
A detailed characterization of microglia-neuron interactions in the α-synuclein PFF mouse model.
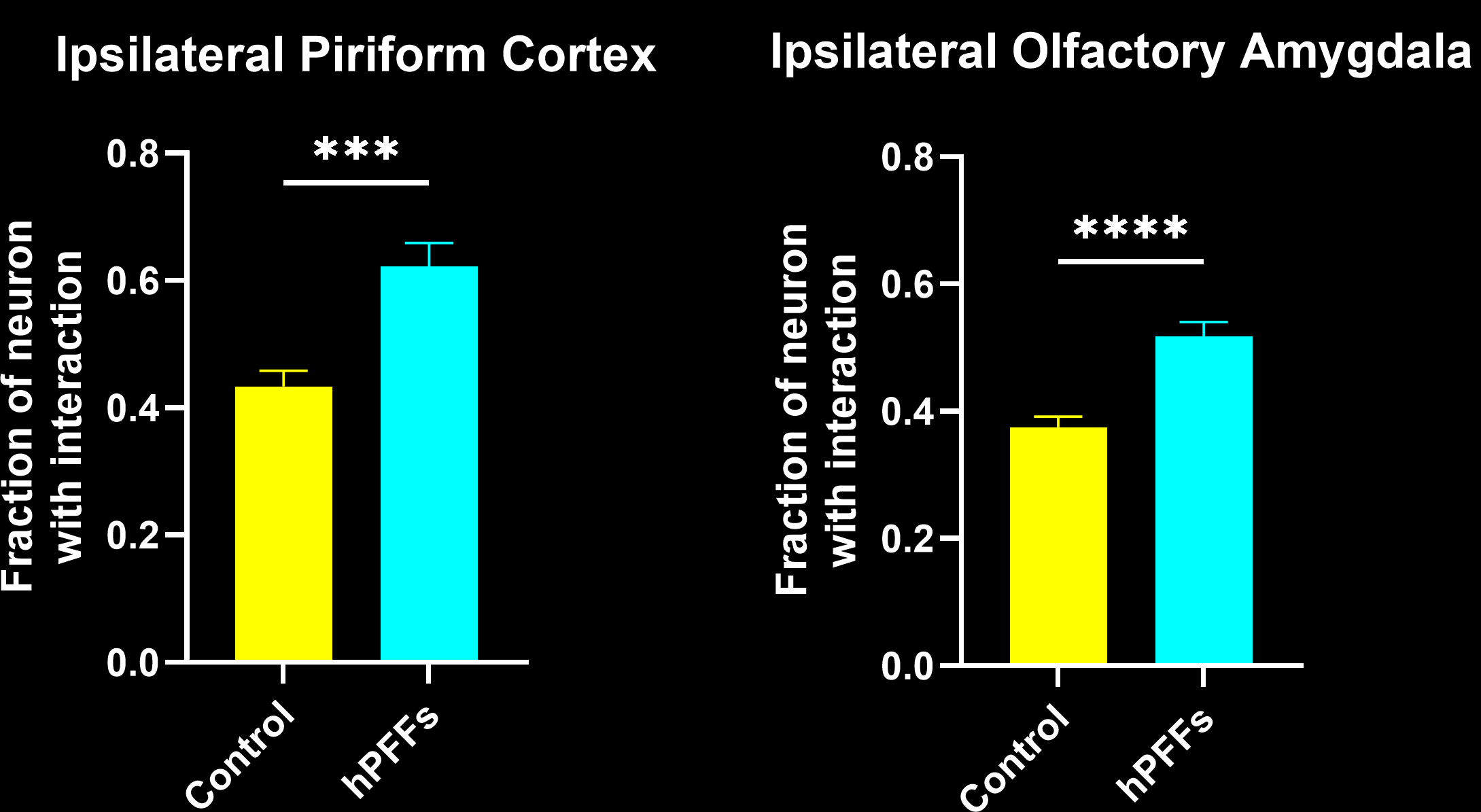
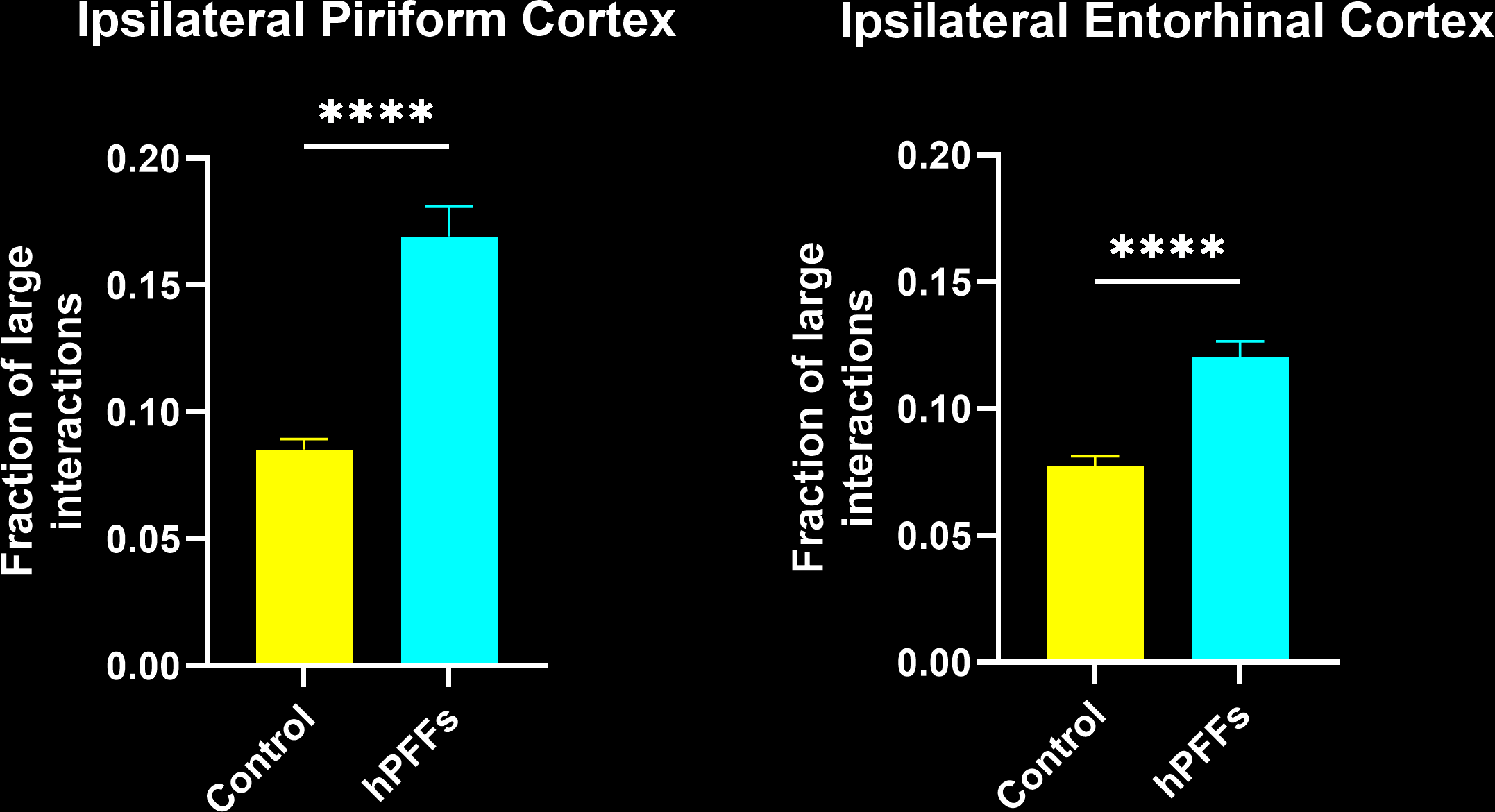
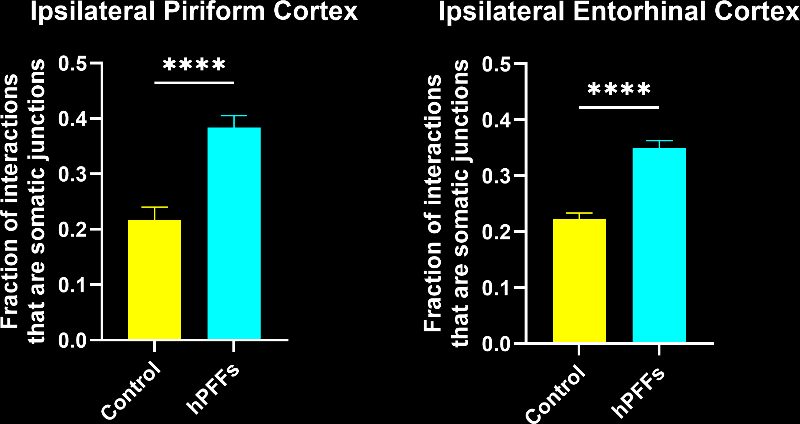
In this research study, the Biospective team has characterized the microglial response to misfolded protein pathology in our α-synuclein PFF model of Parkinson’s Disease. In this study, hemizygous M83 mice were injected unilaterally with human PFFs or PBS (control) into the anterior olfactory nucleus (AON), and were studied 15 weeks post-injection using our proprietary, automated image processing & analysis platform. Additional details of our methods can be found in our "Image Interactive Presentation" below.
In this research study, we found that the hPFF-injected group had, as compared to the PBS control:
- Extensive microgliosis, with the morphological analysis of microglia showing higher sensitivity.
- More microglia-neuron interactions: a larger fraction of neurons have interactions with microglia.
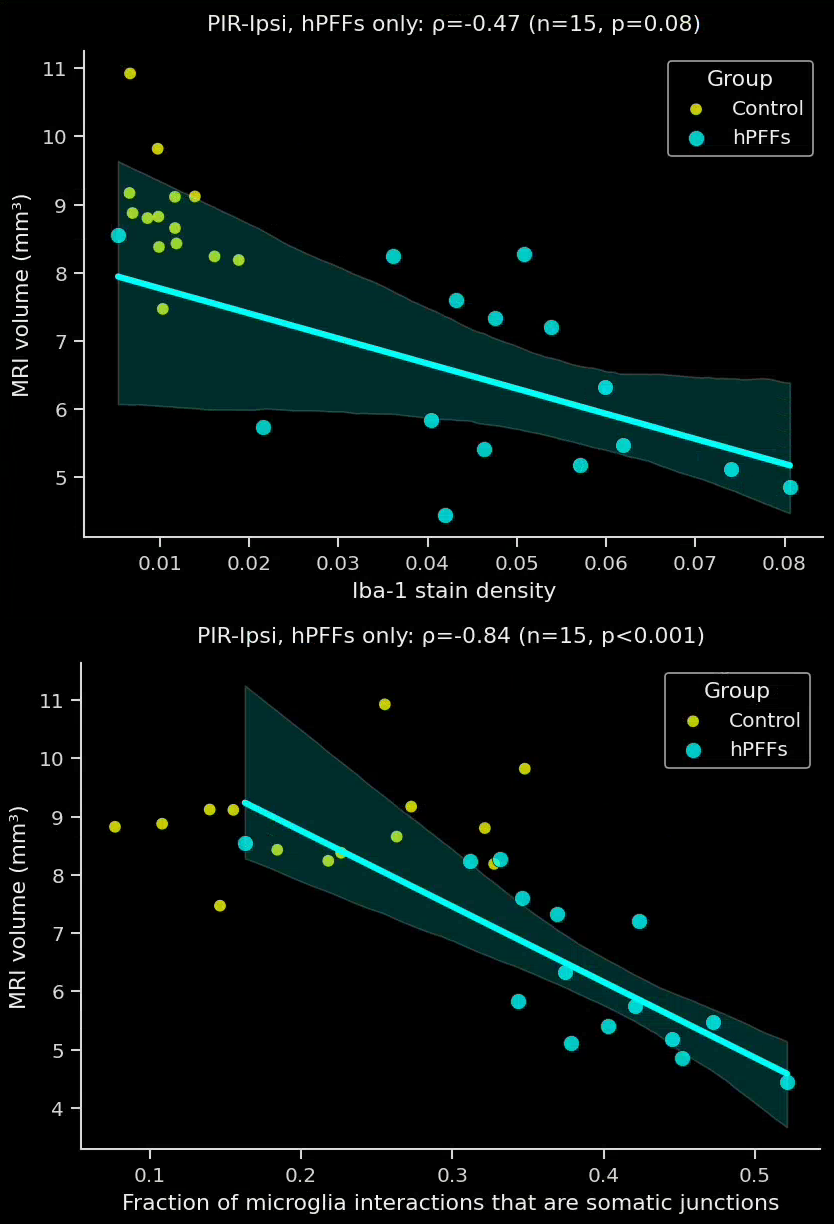
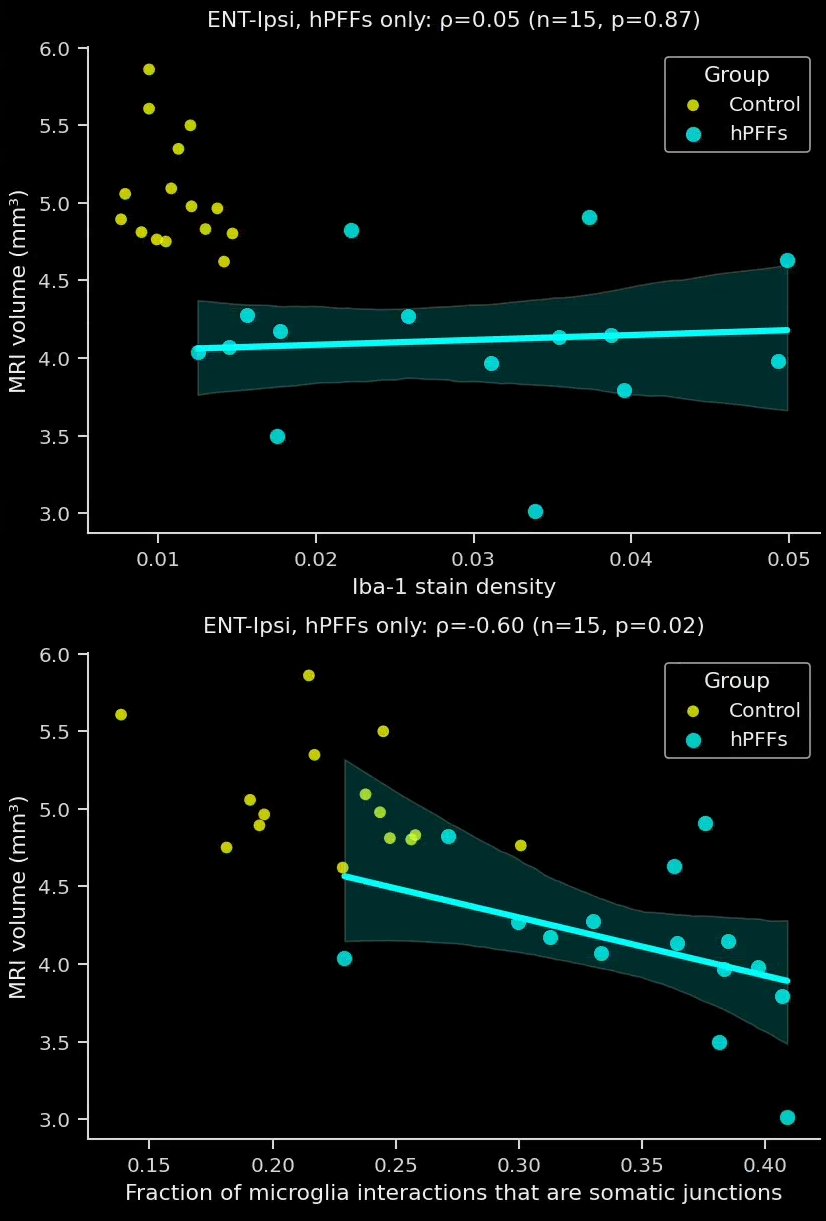
- In the PFF group, the interactions are more extensive and more of these interactions are microglial-process-to-neuronal soma (i.e. somatic junctions) compared to the PBS control group.
- The fraction of interactions that are somatic junctions showed a much stronger correlation to brain atrophy as measured by MRI than the Iba1 stain density.
- These sensitive, advanced metrics can be very attractive for preclinical therapeutic efficacy studies. Metrics with high correlations to translationally relevant clinical endpoints, such MRI brain volume, can provide critical insights into the effects of a putative therapeutic agent.
Interactive Presentation of our Research Study
In the "Image Interactive" below, you can find results on microglia-neuron interactions, including high-resolution Multiplex Immunofluorescence tissue sections of brains from the PFF mouse model and control mice.
How to use Our Interactive Viewer
Navigate through the “Image Story” via the left-hand panel or the on-screen arrows. You can pan around high-resolution microscopy images with your mouse, and zoom in/out using the scroll wheel or the +/- controls. The Control Panel (top-right) allows toggling of image channels and segmentation overlays. For the best experience, we recommend switching to full-screen mode. This Interactive Presentation enables you to explore the model’s neuropathology and associated functional deficits in detail, as if looking directly down the microscope.
Image Interactive describing microglia-neuron interactions, including high-resolution Multiplex Immunofluorescence brain tissue sections, from the α-syn PFF mouse model.
Click to copy link
Biospective's PFF Model Expertise and Services
Biospective is a specialized neuroscience CRO with a focus on Parkinson’s disease models – particularly α-synuclein PFF models, which are a core area of our expertise.
We have spent over a decade developing and executing studies in these models, and to date have performed more preclinical A53T PFF studies than any other CRO. This depth of experience, combined with our scientific rigor, makes us an ideal partner for outsourcing Parkinson’s therapy evaluations. Our team works as an extension of your own, ensuring robust study design and translational relevance at every step.
Some key advantages of partnering with Biospective for synuclein PFF studies include:
-
Unmatched Track Record: 10+ years of continuous experience with α-synuclein PFF mouse models. We have extensively characterized this model and generated large datasets, giving us insight into its nuances and variability. (To our knowledge, we have conducted more A53T PFF studies than any other CRO, underscoring our unique expertise.)
-
In-House A53T Transgenic Colony: We maintain an in-licensed breeding colony of M83 (SNCA*A53T) transgenic mice on-site. Ready access to this colony allows rapid study start-up and large-scale studies (>100 mice) without supply bottlenecks. Non-transgenic littermates or wild-type controls are also available for well-controlled experimental designs.
- Validated Reagents: We use high-quality, sonicated PFFs to ensure study reproducibility.
-
End-to-End Preclinical Services: Biospective provides integrated services from study design through execution and data analysis. Our capabilities include surgical model induction (skilled stereotaxic PFF injections), comprehensive in-life assessments (behavioral testing, motor function assays, etc.), neuroimaging (MRI, PET), bioanalysis (fluid biomarkers, IHC & multiplex immunofluorescence), and expert data interpretation. This one-stop approach ensures consistency and accelerates timelines.
-
Translational Biomarkers & Readouts: We incorporate translational endpoints that bridge preclinical findings to clinical outcomes. For example, we measure neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels in plasma and CSF as a biomarker of neurodegeneration, analogous to what is seen in patients. We also perform MRI brain imaging to quantify neurodegenerative atrophy, and we use quantitative immunohistochemistry (e.g. phospho-α-syn, Iba1 microglial marker) and multiplex immunofluorescence to assess pathology and neuroinflammation at the tissue level. These biomarkers and imaging readouts enhance the translatability of study results to human trials.
-
Global Collaboration & Flexibility: We are a global preclinical neuroscience CRO serving biotech and pharmaceutical clients worldwide. Our scientists collaborate closely with sponsors to tailor studies to specific therapeutic mechanisms or targets. We can accommodate custom endpoints or novel treatment paradigms (e.g. use of patient-derived α-syn fibrils or alternative injection paradigms) – for instance, we have experience using human PD brain extract as the seeding material when required. We also offer flexibility in study design (unilateral vs. bilateral injections, varied post-injection intervals, etc.) to meet your program’s needs. Importantly, we prioritize scientific rigor, reproducibility, and open communication throughout the partnership.
By leveraging these strengths, Biospective enables biotech and pharma teams to generate decision-quality data in the PFF model efficiently. We pride ourselves on fast project initiation, clear data reporting, and supporting our clients across the preclinical phases of drug development.
To fully capitalize on these features, we employ a comprehensive set of validated outcome measures throughout the study. Our evaluations include routine health and clinical observations (e.g. body weight tracking and clinical scoring), detailed behavioral testing and motor function assays, and sleep studies to capture phenotypic changes. We perform in vivo MRI to monitor neurodegenerative changes (such as volumetric brain atrophy) longitudinally, and we analyze biofluids (blood, CSF) for biomarkers like NfL as quantitative readouts of neurodegeneration. For terminal endpoints, we carry out extensive histopathological analysis: immunohistochemical (IHC) and immunofluorescence staining for phospho-α-synuclein inclusions, markers of neuronal loss (e.g. NeuN), and glial activation markers (Iba1 for microglia, GFAP for astrocytes), followed by quantitative digital image analysis. By integrating these multi-modal readouts, we obtain a rich data package on pathology, biochemical changes, and functional impairment, providing a holistic view of how a therapeutic impacts the disease processes in the model.
Accelerating Preclinical Parkinson’s Therapeutic Testing
Biospective’s α-synuclein PFF mouse models are ideal for efficacy testing, biodistribution studies, mechanism-of-action investigations, and target engagement evaluation of new Parkinson’s disease therapies.
We have successfully employed this research disease model to test a wide range of therapeutic modalities, including small molecule neuroprotective compounds, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), gene therapies (e.g. AAV vectors), and antibody or vaccine-based immunotherapies. The model’s versatility – in recapitulating both motor and non-motor aspects of PD and providing measurable biomarkers – allows us to tailor study endpoints to the specific mechanism of action of the therapy being tested. For example, we can assess target engagement by measuring reductions in α-syn pathology burden or changes in downstream signaling; we can evaluate biodistribution and pharmacodynamics by sampling tissues and fluids at various time points; and of course, we determine therapeutic efficacy by improvements in motor function, histopathology, and biomarker profiles relative to controls.
By partnering with Biospective, pharmaceutical and biotech researchers gain access to a thoroughly characterized, translationally relevant PD model and the scientific expertise to utilize it optimally. We aim to de-risk and accelerate your drug development program by providing decision-ready data in the context of a model that closely mirrors human disease. Our scientific team will work closely with yours to design studies that answer your key questions – whether it is proof-of-concept efficacy, dosing paradigm optimization, or mechanistic exploration – and to execute those studies with utmost quality and rigor.
In summary, Biospective offers a unique combination of a cutting-edge Parkinson’s disease animal model and deep scientific know-how. Our α-synuclein PFF mouse model, coupled with our end-to-end preclinical CRO capabilities, positions us to be a valued preclinical partner in advancing novel Parkinson’s therapies. We are committed to helping you translate therapeutic hypotheses into compelling in vivo evidence, and ultimately, to speeding promising treatments toward clinical success. Let our experienced team and robust models support your next breakthrough in Parkinson’s disease research.
Learn more about our characterization of the alpha-synuclein PFF model, our validated measures, and our Parkinson's disease CRO services.
Discover more of our Parkinson's Disease Models
Related Content
Up-to-date information on Parkinson's Disease and best practices related to the evaluation of therapeutic agents in PD animal models.
Neurofilament Light Chain in Parkinson's Disease Models
How neurofilament light chain (NfL; NF-L) levels can be used as blood (plasma; serum) & CSF biomarkers in Parkinson's disease mouse and rat models.
AAV α-Synuclein Models for Parkinson's Disease Drug Development
Overview of adeno-associated virus (AAV) induced α-synuclein expression in mouse & rat models for use in preclinical studies of disease-modifying therapeutics.
Microglial Activation in an α-Synuclein PFF Mouse Model
We have quantified microglial activation, based on morphology, in an α-synuclein preformed fibril (PFF) seeding & spreading mouse model of Parkinson’s disease.