Biospective is an industry leading provider of high-throughput neuroscience-centric immunohistochemistry services for biotech, pharma, and academic researchers globally. We have deep specialization in mouse & rat models of neurological and neuromuscular diseases with an extensive track record. We leverage our fully integrated platform (IHC staining → whole‑slide scanning → quantitative image analysis) to provide disease model-driven IHC services with pharma-grade rigor.
Our Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Services
High throughput immunohistochemistry staining and spatial analysis of tissues from research animal models.
As a Preclinical CRO, we provide Contract Research Services for immunohistochemistry staining and analysis to:
- Academic Labs & Research Centers
- Biotech Companies
- Pharmaceutical Industry
We are leaders in:
- IHC staining
- Whole slide scanning
- Quantitative image analysis of digitized tissue sections
Our team has decades of experience with:
- Brains
- Spinal Cords
- Muscles
- Peripheral nerves
- Ganglia

IHC Staining of NeuN in the Mouse Brain.
Representative coronal section of FFPE section of adult mouse brain stained for NeuN using chromogenic AEC detection. This staining allows for assessment of neuronal density, cortical architecture, regional neuron distribution, and disease-related neurodegeneration.
Our Laboratory Facilities leverage state-of-the-art automated IHC/IF staining instruments and high-throughput whole slide scanners to maximize quality and minimize turnaround times.
If you are collecting tissues as part of your in-house studies or animal model studies performed with another vendor, you can simply them to us for staining, slides scanning, and image analysis.
Example IHC Studies from Mouse Models of Neurological Diseases
At Biospective, we routinely perform studies in mouse models of ALS, Alzheimer's Disease & Tauopathies, Parkinson's Disease, and Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Here we show some illustrative examples of our IHC staining from these models. You can also learn more about our IHC Services for these models using the provided links.
IHC Staining in ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis) Animal Models
We have extensive experience performing IHC staining in animal models of ALS.

Phosphorylated (p409/410) TDP-43 Staining in "Low Dox" rNLS8 Mice.
High magnification view of a brain tissue section from Biospective's "Low Dox" TDP-43ΔNLS (rNLS8) mouse model stained for phospho-TDP-43 (p409/410) using AEC chromogenic detection with Acid Blue 129 counterstain (Zehntner, 2008).
In these ALS models, we routinely stain brains and spinal cords for:
- Human TDP-43
- Phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43)
- GFAP (astrocytes)
- Iba1 (microglia)
- ATP5A (mitochondria)
- Spinal motor neurons (ChAT)
Our team has developed robust image analyses for ALS models:
- Please see our Interactive Presentation – Multiplex Immunofluorescence of Brain Sections from the “Low Dox” TDP-43ΔNLS Mouse Model of ALS.
- We can also use multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) to stain the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) in the muscle - see our "Image Interactive" entitled Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) Denervation in the TDP-43ΔNLS (rNLS8) Mouse Model of ALS.
If you have brains, spinal cords, muscle, or other tissue from TDP-43 models and/or other models of ALS (e.g. SOD1, C9orf72, PFN1), we will be happy to work with you.
We can also complement IHC staining by fluid biomarkers from blood and CSF, such as:
You can learn more about these biomarkers on our Fluid & Cell Biomarkers Services page.
IHC Staining in Alzheimer's Disease & Tauopathies Animal Models
We have validated IHC staining & image analysis protocols for amyloid-beta and tau markers, as well as neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.

Amyloid-β and Tau Staining in Brains of Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease & Tauopathies.
(Left) High magnification view of the brain of an APP/PS1 transgenic mouse at 9 months-of-age stained for fibrillar amyloid-beta showing Aβ plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
(Right) High magnification view of the brain of a PS19 (P301S) transgenic mouse 3 months following injection of Tau preformed fibrils (PFFs) showing localized AT8-positive tau aggregates and their distribution within affected brain structures.
In these Alzheimer's Disease & Tauopathy models, we routinely stain brains for:
- Amyloid-beta (various Aβ antibodies)
- Phosphorylated Tau (AT8)
- Conformationally-altered Tau (MC1)
- GFAP (astrocytes)
- Iba1 (microglia)
- NeuN (neurons)
- ASC (inflammasome)
Our team has developed robust image analyses for Alzheimer's disease models, including:
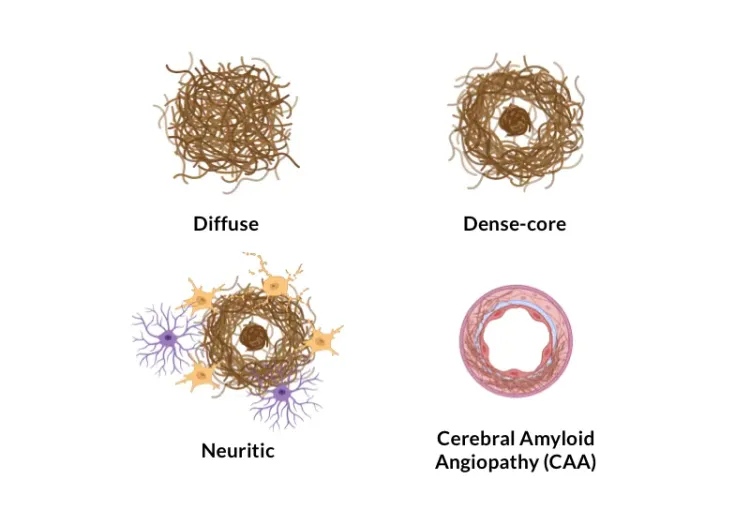
- Amyloid plaque characterization (e.g. size, type [compact, diffuse, fibrillar], count);
- See our Service: Amyloid Plaques Histology Services
- See our Resource: Amyloid-β Plaque Analysis in Alzheimer's Disease
- Inflammatory microenvironment analysis; see our Innovation: Amyloid-β & the Inflammatory Microenvironment in an APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
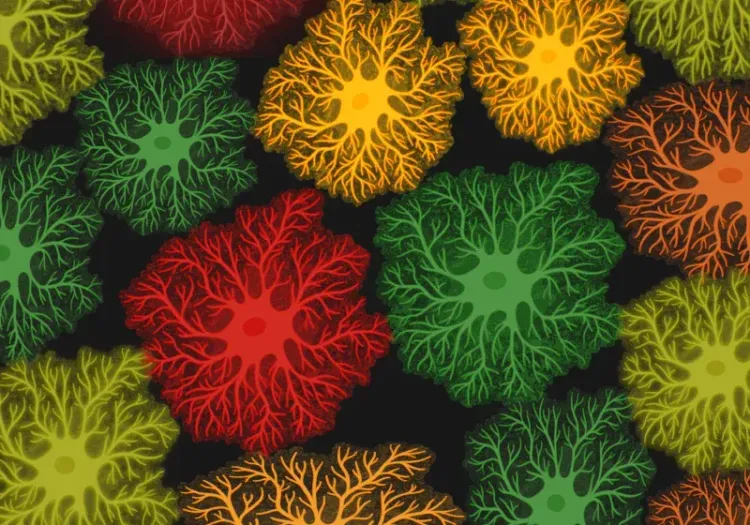
- Reactive astrocyte analysis; see our Innovation: Astrocytes & Amyloid-β Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease
Please also see our Interactive Presentation – Tau, Rather than Amyloid-β, Drives Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Mouse Models of AD.
If you have brains or other tissue from APP/PS1 mice and/or other mouse or rat models of Alzheimer's disease or tauopathies (e.g. 5xFAD mice, PS19 mice, APP KI mice or rats, JNPL3 mice, rTg4510 mice), we will be happy to work with you.
We can also complement IHC staining by fluid biomarkers from blood and CSF or brain homogenate supernatants, such as:
- Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L)
- Aβ40 and Aβ42
- Total tau and phosphorylated tau
- GFAP
- Cytokines (e.g. IL-1β, TNF-α)
- Chemokines
- APOE4
- PSD-95
You can learn more about these biomarkers on our Fluid & Cell Biomarkers Services page.
IHC Staining in Parkinson's Disease Animal Models
We have a wide variety of validated markers for animal models of Parkinson's disease, including α-synuclein and tyrosine hydroxylase (dopaminergic neurons).

pSyn Staining in PFF-Injected M83 Mouse Brain
High magnification view of pSyn129 staining in Biospective's alpha-synuclein PFF seeding & spreading mouse model of Parkinson's disease showing dense pSyn-positive aggregates and their localized accumulation within affected neurons.
In these Parkinson's Disease models, we routinely stain brains for:
- Phosphorylated α-synuclein (pSyn129)
- GFAP (astrocytes)
- Iba1 (microglia)
- NeuN (neurons)
- Tyrosine hydroxylase (dopaminergic neurons)
Our team has developed robust image analyses for Parkinson's disease models, including:
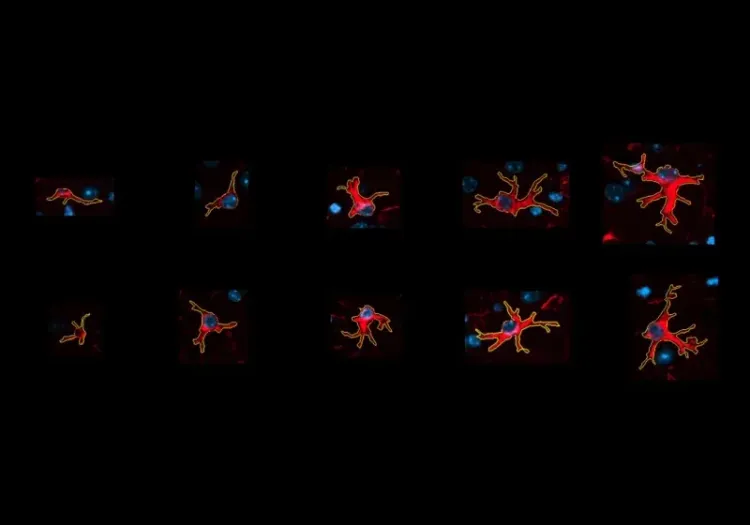
- Activated microglia; see our Innovation: Microglial Activation in an a-Synuclein PFF Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease
If you have brains from α-synuclein and/or other transgenic, knock-in, knock-out, humanized, or inducible toxin (e.g. 6-OHDA, MPTP, rotenone) mouse or rat models of Parkinson's disease, we will be happy to work with you.
We can also complement IHC staining by fluid biomarkers from blood and CSF or brain homogenate supernatants, such as:
- Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L) [also see our Resource - Neurofilament Light Chain in Parkinson's Disease Models]
- GFAP
- Cytokines (e.g. IL-1β, TNF-α)
- Chemokines
- PSD-95
You can learn more about these biomarkers on our Fluid & Cell Biomarkers Services page.
IHC Staining in Multiple Sclerosis Animal Models
We have standardized protocols for myelin, peripheral inflammation, and neuroinflammation in animal models of multiple sclerosis (MS).

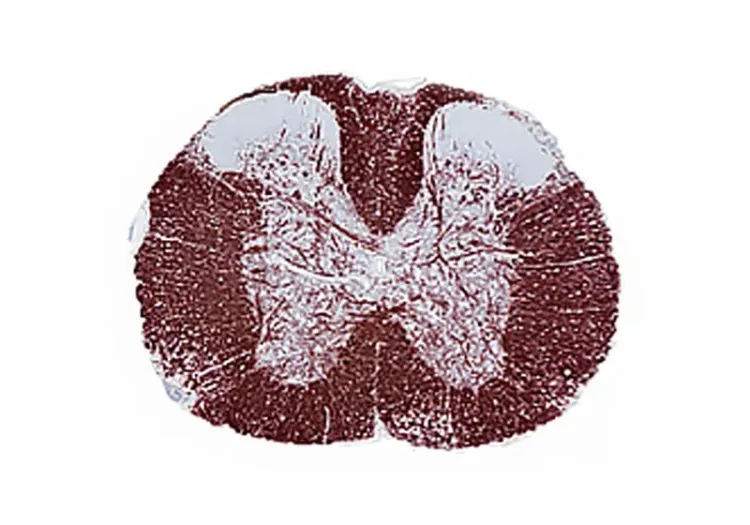
MBP and Iba1 Staining in Demyelination/Remyelination and Autoimmune-Mediated Inflammation Models
(Left) Representative coronal section of mouse brain from the cuprizone mouse model of demyelination & remyelination stained for Myelin Basic Protein (MBP). Whole slide brightfield imaging enables visualization of myelin integrity and regional patterns of demyelination & remyelination.
(Right) Representative transverse section of spinal cord from an EAE (Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis) mouse model of autoimmune-mediated demyelination mouse stained for Iba1 to detect activated microglia and infiltrating macrophages.
In these Multiple Sclerosis (MS) models, we routinely stain brains and spinal cords for:
- MBP, MOG, or PLP (myelin)
- GFAP (astrocytes)
- Iba1 (microglia & macrophages)
- CD3 (T cells)
- Mature oligodendrocytes
- Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells (OPC) markers
- Axonal injury markers
Our team has developed robust image analyses for MS models, including:
- Markers of axonal injury & damage; see our Resource: Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Axonal Injury
We can also complement IHC staining by fluid biomarkers from blood and CSF or brain homogenate supernatants, such as:
- Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L) [also see our Resource - Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Axonal Injury]
- GFAP
- Cytokines (e.g. IL-1β, TNF-α)
- Chemokines
- PSD-95
You can learn more about these biomarkers on our Fluid & Cell Biomarkers Services page.
If you have brains, spinal cords, or other tissue from EAE, cuprizone, and/or other mouse or rat models of Multiple Sclerosis (e.g. LPC), we will be happy to work with you.
Summary of IHC Staining in Neurological Diseases Models
|
Model/Disease |
Key IHC Markers |
Typical Readouts |
Related Endpoints & Services |
|
ALS |
TDP-43, pTDP-43, GFAP, Iba1, ChAT |
TDP-43 pathology, neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration |
Motor function, muscle strength, EMG, CT muscle atrophy, MRI brain atrophy, blood & CSF NF-L, NMJ analysis |
|
Alzheimer's Disease & Tauopathies |
Aβ, pTau (AT8), MC1, GFAP, Iba1 |
Plaque burden, tau aggregates, microgliosis, astrogliosis |
Amyloid microenvironment analysis, MRI brain atrophy, fluid biomarkers |
|
Parkinson's Disease |
pSyn129, TH, GFAP, Iba1, NeuN |
pSyn burden, dopaminergic neuron loss, neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration |
Sleep, motor function, MRI brain atrophy, blood & CSF NF-L |
|
Multiple Sclerosis |
MBP/MOG/PLP, Iba1, GFAP, CD3 |
Demyelination / remyelination, axonal injury, neuroinflammation, peripheral inflammatory infiltrates |
Clinical scores (e.g. EAE scores), tissue & fluid cytokine analysis, MRI (MTR analysis), blood & CSF NF-L |
This table provides a summary of key IHC markers, typical readouts, and related endpoints & services across ALS, Alzheimer's Disease & Tauopathies, Parkinson's Disease, and MS models.
What is Immunohistochemistry (IHC)?
An overview of the IHC technique and its value for spatial analysis in animal models of neurological and neuromuscular diseases.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a key technique in preclinical neuroscience research, enabling visualization and quantification of specific proteins within tissue. Using antibodies tagged with a variety of reporter systems, IHC maps protein localization, expression levels, and cellular distribution (Velasco-Vales, 2022; Mebratie, 2024). In neurodegenerative disease studies, IHC is indispensable for characterizing protein misfolding, neuroinflammation, neuronal loss, synaptic dysfunction, and circuit pathology, supporting evaluation of disease progression and therapeutic interventions.

Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining of the Mouse Substantia Nigra for Dopaminergic Cell Bodies & Processes (left) and Neuronal Nuclei (right).
At Biospective, our laboratories utilize multiple automated IHC/IF staining instruments, ensuring:
- High reproducibility
- Low variability
- Rapid turnaround
- Optimal consistency across large cohorts
We maintain well-validated IHC panels for rodent models of neurological diseases and can develop custom staining protocols tailored to your research needs. Our dedicated R&D team of experienced scientists and technicians ensures that every protocol is optimized for reproducibility, sensitivity, and high-quality quantitative analysis.
What is the difference between IHC and IF?
A comparison of immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques.
|
Feature |
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) |
Immunofluorescence (IF) |
|
Multiplexing |
Limited (1-2 markers) |
High (multiple fluorophores) |
|
Detection |
Enzyme-based chromogenic |
Fluorophore emission |
|
Visualization |
Brightfield |
Widefield Epi-fluorescence / Confocal |
|
Dyes |
DAB, AEC, Fast Red |
FITC, TRITC, Alexa Fluor, DAPI |
|
Signal |
Permanent |
Prone to photobleaching |
|
Quantification |
Semi-quantitative |
Highly quantitative |
|
Background |
Low |
Autofluorescence possible |
|
Sensitivity |
Moderate |
High |
|
Samples |
FFPE or frozen tissues |
FFPE & frozen tissue; cultured cells |
|
Output |
Colorimetric |
Fluorescent |
A comparison of characteristics of Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence (IF) across key criteria, including multiplexing, detection, visualization, dyes, signal, quantification, background, sensitivity, samples, and output.
To learn more about our Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Services
Related Content
Up-to-date information on our Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Services and best practices related to the evaluation of therapeutic agents in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases.
Amyloid-β Plaque Analysis in Alzheimer's Disease
Overview of methods to classify & quantify Aβ plaques in brain tissue sections from humans & Alzheimer’s disease animal models (transgenic mice & rats).
Amyloid-β & Inflammatory Microenvironment in Alzheimer's Mice
We have analyzed the complex spatial relationships between β-amyloid plaques, activated & resting microglia, and astrocytes in an APP/PS1 transgenic model.
TDP-43 ΔNLS (rNLS8) Mice for ALS Drug Development
This resource provides information about the use of the ΔNLS (deltaNLS, hTDP-43ΔNLS, hTDP-43DeltaNLS, dNLS, TDP43 NLS, rNLS8) TDP-43 transgenic mouse model of ALS for preclinical therapeutic studies.
Astrocytes & Amyloid-β Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease
Analysis of astrocyte morphology in the amyloid-β plaque microenvironment provides a sensitive measure of disease progression in transgenic mice.
ALS Mouse Models & Spinal Motor Neurons
An overview of the involvement of spinal motor neurons in disease progression in mouse models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).
Astrocyte Morphology in Alzheimer's Disease
An overview of astrocyte morphological analysis and the applications to neurodegenerative disease research and drug discovery & development.
Demyelination & Remyelination in the Cuprizone Model
An overview of the methods available to measure myelin and oligodendrocytes in the cuprizone demyelination mouse model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) & Axonal Injury
This resource describes the methods available for measuring axonal damage & axon degeneration, including tissue markers and plasma & CSF neurofilament light chain (NfL; NF-L) levels, in the EAE model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
Microglial Morphology Analysis in Spinal Cords from C9orf72 ALS Patients
Tamara Graveson, M.D., Ph.D. and Philip Ramos, Ph.D. RIKEN Center for Brain Science, Wako, JapanImaging and morphometric analysis of spinal cord tissue from C9orf72 ALS patients reveal changes in microglial morphology and distribution.
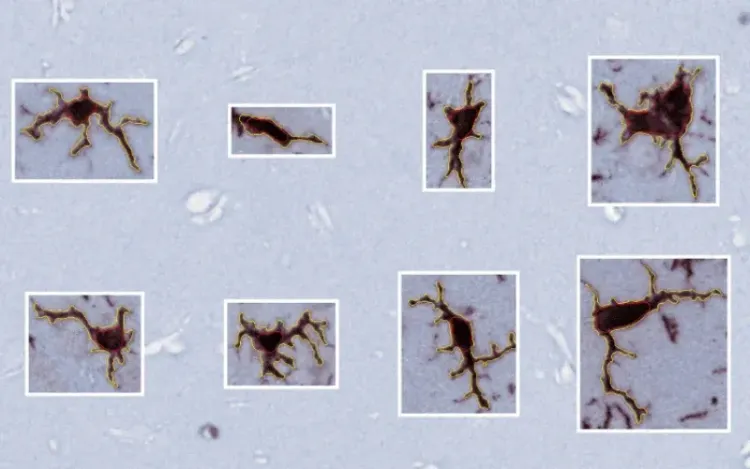
Microglia Morphology in ALS, Alzheimer's Disease & Parkinson's Disease
An overview of microglial morphological analysis and the applications to neurodegenerative disease research and drug discovery & development.
Microglia-Neuron Interactions & Neurodegenerative Diseases
A concise review of the direct interactions between microglia & neurons, and how these cell-to-cell interactions may be affected in neurodegenerative diseases.