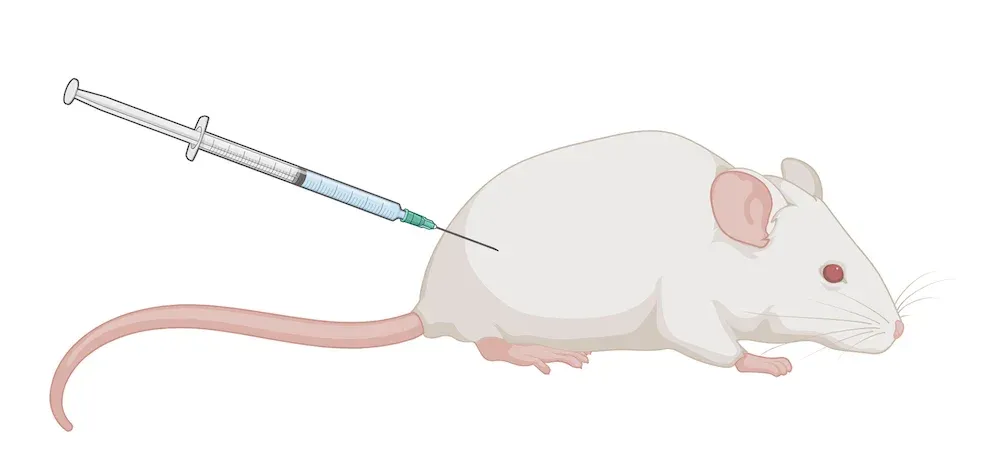
Peripheral Administration
We can deliver therapeutic agents via several peripheral routes of administration, including intravenous (i.v.), intraperitoneal (i.p.,), subcutaneous (s.c.), intramuscular (i.m.), and intranasal (i.n.). We work closely with our Sponsors to determiner the best method of delivery.
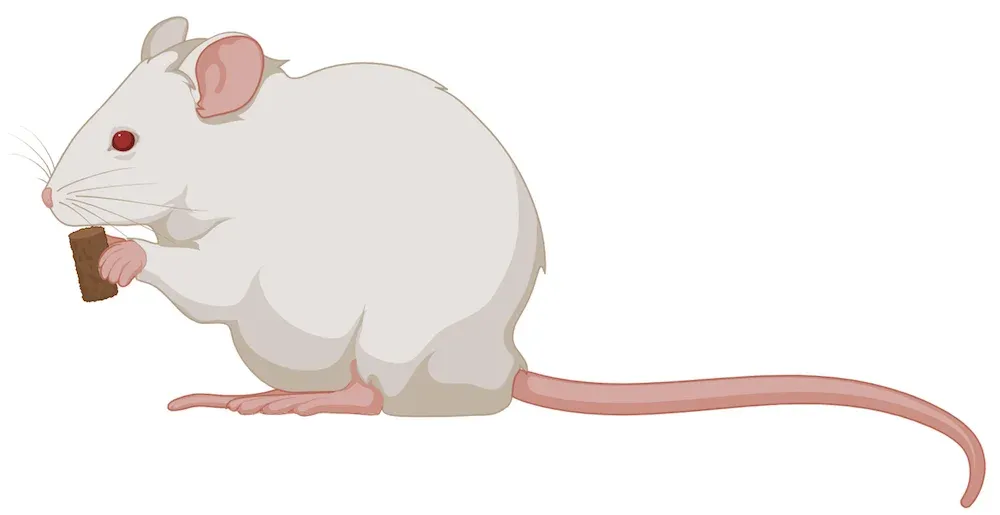

Oral Administration
For therapeutics that can be delivered orally (p.o.), there are several options. Our team is thoroughly experienced in delivery via oral gavage. Compounds can also be delivered in the chow or drinking water. In this case, we closely monitor the animal's intake.
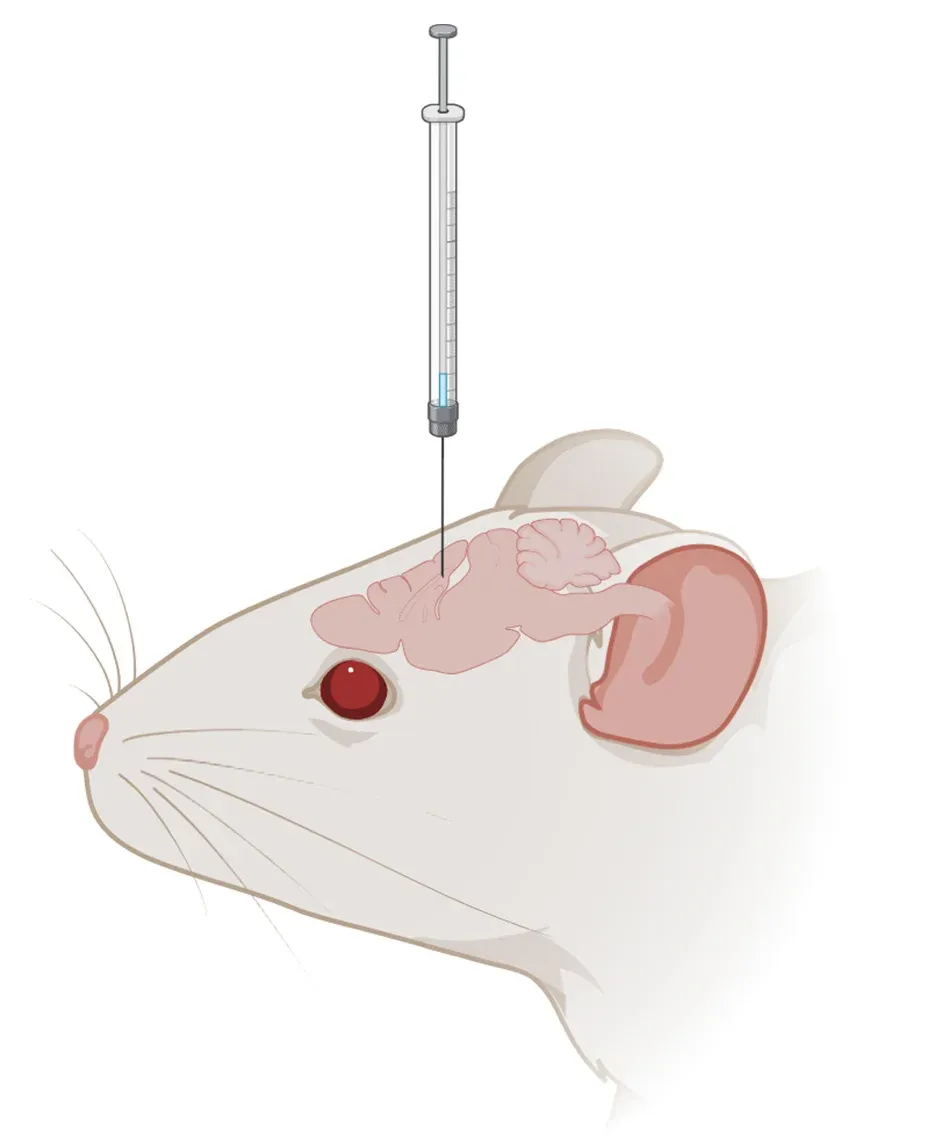
Direct CNS Administration
For therapeutic agents that do not readily cross an intact blood-brain barrier (BBB), we can administer them directly into the CNS (brain, spinal cord, or CSF). Several routes are available, including intracerebral (i.c.), intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.), intra-cisterna magna (i.c.m), lumbar puncture (l.p.), or intraspinal (i.s.). If repeated or chronic administration is required, a catheter can be inserted.
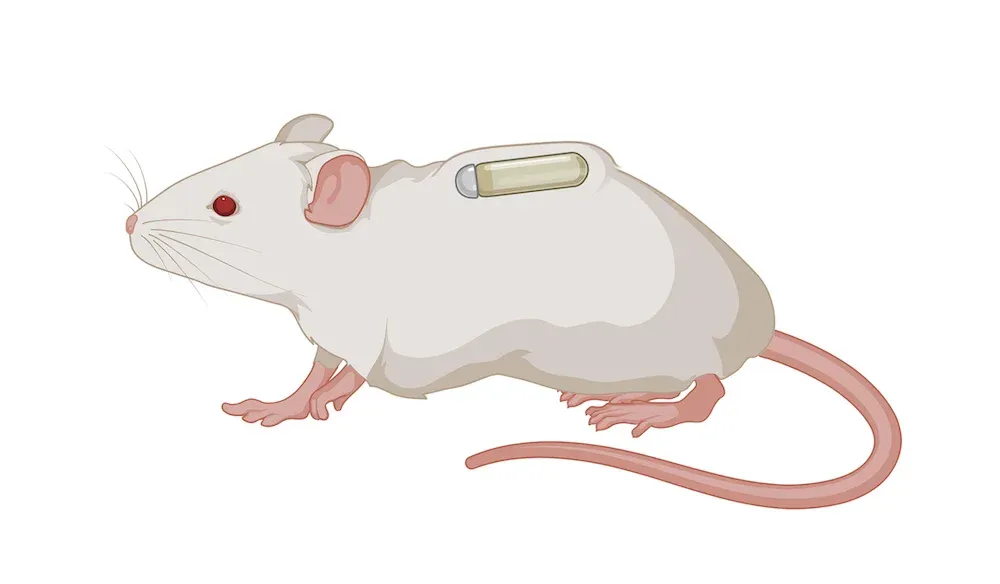
Osmotic Pump Administration
For long-term delivery of therapeutic agents, we can use an osmotic pump. Pumps are available in various sizes with different flow rates. They are typically implanted subcutaneously and can be coupled with a catheter (e.g. for continuous i.c.v. administration).
Learn more about our Dosing Services.