CNAP (Sensory)
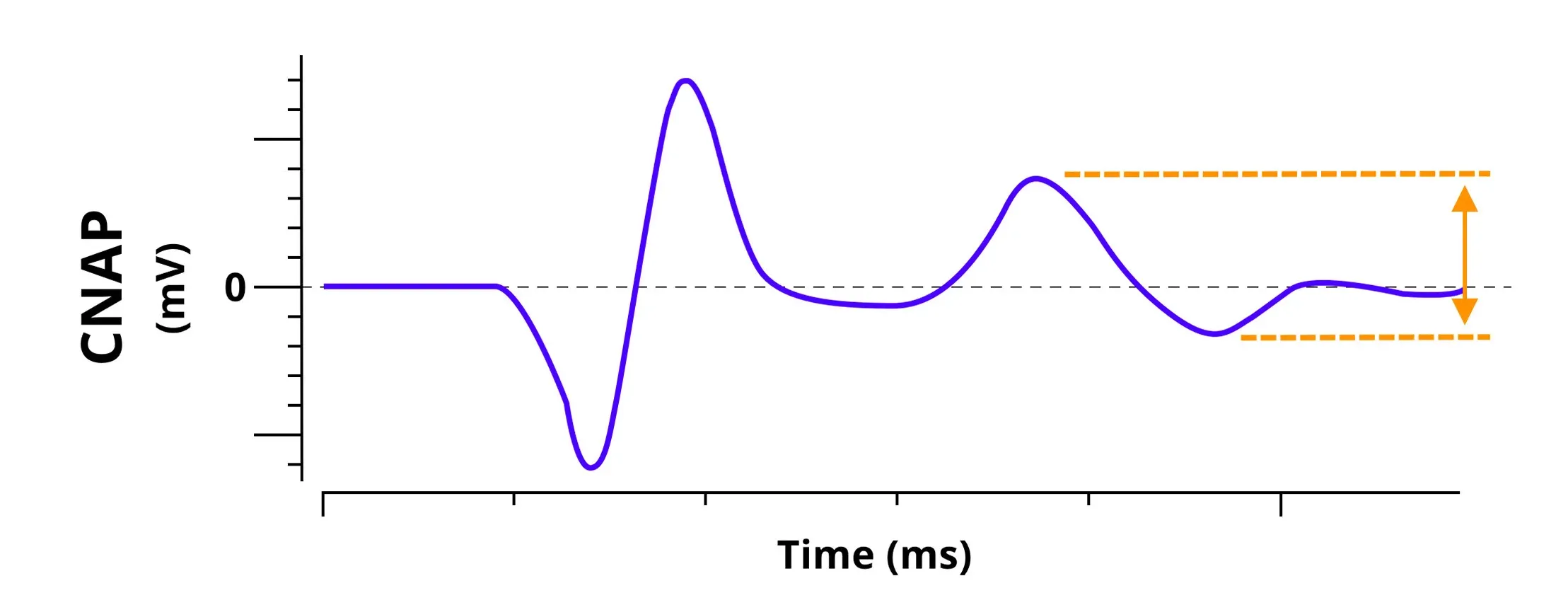
The Compound Nerve Action Potential (CNAP) measures the activity of all fibers comprising a stimulated peripheral nerve. The principle is to electrically stimulate a nerve trunk and to record, in return, the compound action potential resulting from the activity of all fibers. It serves as an excellent measure to assess the integrity and functionality of nerves in animal models.
Changes in CNAP parameters, such as reduced amplitude or altered conduction velocities, may indicate nerve damage, demyelination, or dysfunction. As such, CNAP is a valuable tool for evaluation of the effects of experimental treatments.
Learn more about our CNAP Services.