Biospective’s EAE mouse models facilitate multiple sclerosis (MS) drug development with translational MS pathology for preclinical research. As a neuroscience CRO with extensive experience with EAE models, we offer comprehensive in vivo services — including therapeutic efficacy (with positive controls), mechanism-of-action, and target engagement — supported by clinically relevant biomarkers, including neurofilament light chain (NfL) and cytokine concentrations, and quantitative multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF).
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) is considered a gold-standard model for multiple sclerosis drug development studies. This mouse model reliably demonstrates autoimmune-driven demyelination, neuroinflammation, and axonal damage (see our Resource - EAE & Axonal Injury) reflecting key pathologic features of human MS. At Biospective, we have rigorously validated measures of motor impairment (EAE Score), muscle weakness, blood & CSF biomarkers, and quantitative IHC & multiplex immunofluorescence markers (e.g. MBP, Iba1, GFAP, CD3, CD45) for this MS model to generate pharma-grade data for our sponsors around the world.
Overview of the EAE Mouse Model of MS
A gold-standard animal model of MS for preclinical drug development.
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a widely-used animal model for assessing therapeutic agents targeting autoimmune-mediated central nervous system (CNS) disease. EAE induction is most commonly performed by immunizing mice against myelin-derived antigens, such as:
- Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG35-55 or MOG1-125)
- Myelin Basic Protein (MBP)
- Proteolipid Protein (PLP)
EAE mice model several key aspects of human MS, including the following key pathologic features:
- Focal Demyelination: Loss of myelin (e.g. MBP staining) is found throughout the spinal cord.
-
Peripheral Inflammatory Infiltrates: Lymphocytes (e.g. T cells) and macrophages are observed in demyelinating lesions.
-
Neuroinflammation: Activated microglia and reactive astrocytes are present in addition to the peripheral inflammatory infiltrates.
- Axonal injury/damage & axon degeneration: Axonal injury is a key feature of EAE, resulting in the release of neurofilament light chain into CSF and blood.
The EAE model of multiple sclerosis demonstrates motor symptoms, such as paralysis, which recapitulates clinical symptoms seen in MS patients. The EAE animal model is characterized by a progressive paralysis followed by full or partial recovery, which may then be relapsing-remitting or chronic depending on the specific antigen used.
A key advantage of the EAE mouse model for MS drug development is the availability of well-established positive controls, including dexamethasone and fingolimod. The inclusion of these drug controls in preclinical studies allows for benchmarking of therapeutic effects.
EAE Model Generation & Study Timelines
Biospective is able to perform a range of study sizes, from pilot to large-scale studies.
We most frequently use the MOG35-55 (MOG EAE) model in C57BL/6 mice, which is a well-established, chronic model of multiple sclerosis that is advantageous for therapeutic studies injection of MOG35-55 peptide with Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA) and pertussis toxin (PTx) on a defined schedule to produce a T cell-mediated autoimmune disease.
Following MOG-EAE induction, mice demonstrate hindlimb paralysis and spinal cord pathology. Various fluid-based biomarkers (e.g. neurofilament light chain, inflammatory cytokines) can be found in the CSF collected from the cisterna magna of EAE mice.
The in-life phase of EAE mouse model studies typically range from 14-35 days, depending on the phase of disease (e.g. peak vs. chronic) for tissue collection and analysis. We work closely with our sponsors to identify the optimal design based on the target(s) and mechanism(s) of action of their therapeutic agents.
Validated Endpoints & Translational Biomarkers
Biospective has implemented a suite of validated endpoints and MS relevant biomarkers to enable clinical advancement of therapeutic programs.
To fully characterize EAE mice and assess treatment outcomes, Biospective has validated a broad spectrum of endpoints – encompassing behavioral assays, fluid & tissue biomarkers, and histopathology. This comprehensive approach yields robust, quantitative readouts for both efficacy and mechanism-of-action in preclinical studies. Key validated endpoints in our EAE mouse model include:
Behavioral & Functional Endpoints
- Body Weight: Changes in weight typically track well with disease severity in EAE mice.
-
EAE Score: A sensitive, standardized scoring system that assesses the clinical disease progression in EAE mice.
-
Grip Strength Test: Uses a grid or a bar attached to a force-sensing device (grip strength meter) to measure the maximum force exerted by the animal before losing its grip as it is pulled away from the instrument.
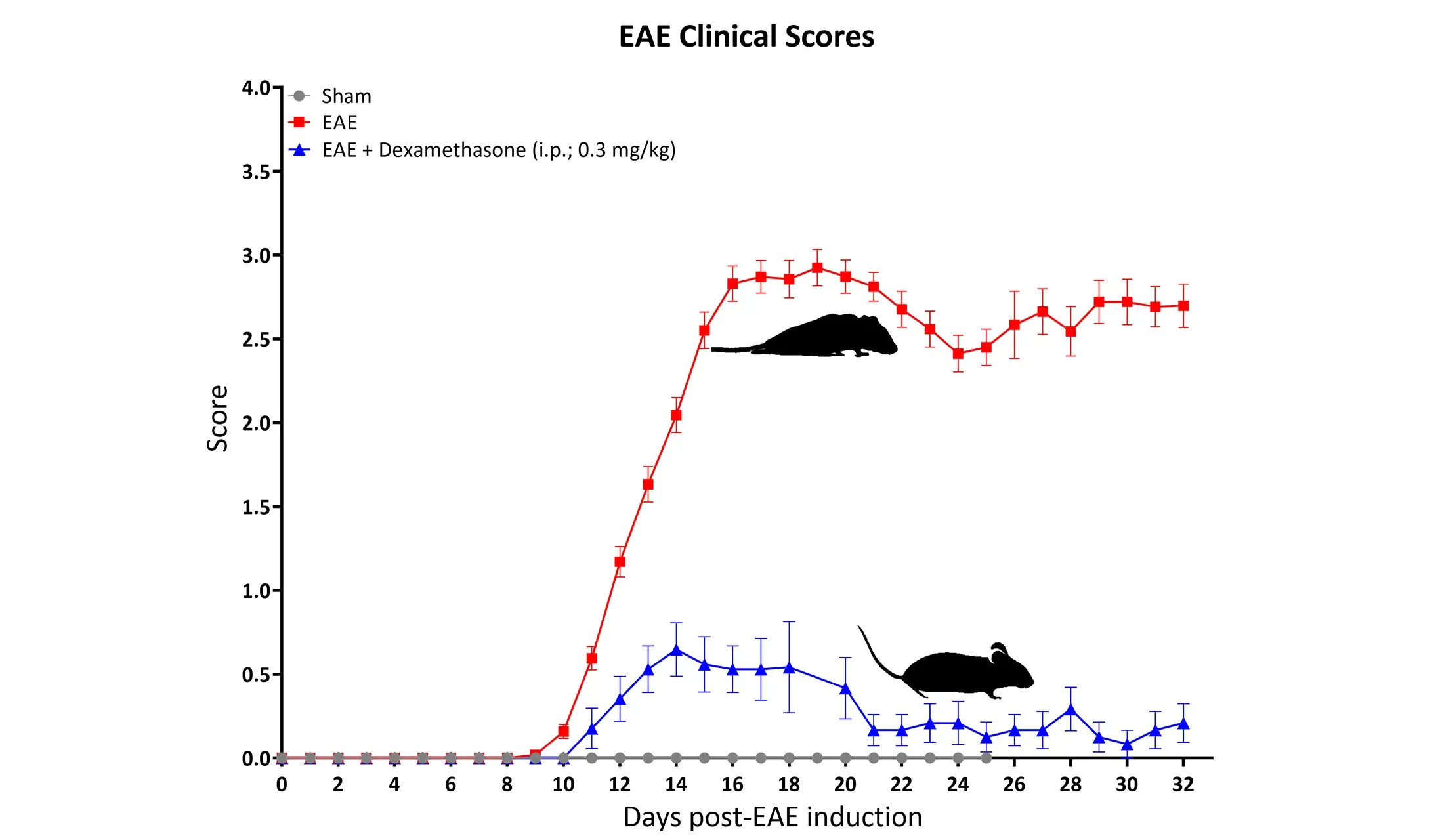
EAE scoring performed on the MOG35-55 EAE C57BL/6 mouse model. Note the significantly attenuated disease in the positive control group of mice, which nicely demonstrates the ability to show disease modification in this MS model.
Fluid & Tissue Biomarkers
- CSF & Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain (NfL): A fluid biomarker of axonal damage and neurodegeneration, measured in cerebrospinal fluid (and optionally blood plasma). Elevated NfL levels indicate ongoing neuronal injury; this biomarker is also used in clinical trials, making it a valuable bridge between preclinical and clinical results.
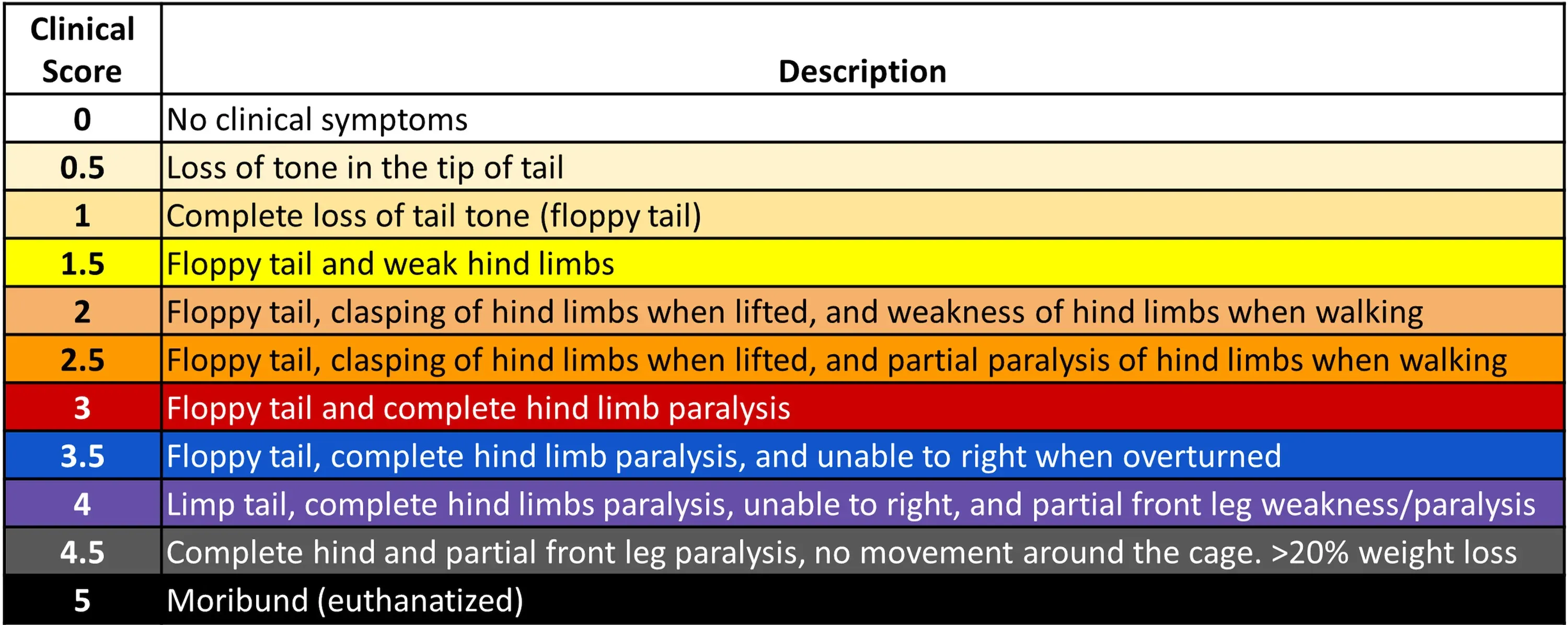
- Quantitative Histopathology (IHC/mIF) of Spinal Cord: High-resolution tissue analyses to quantify MS-related pathology. We perform immunohistochemistry (IHC) and multiplex immunofluorescence for markers such as myelin (MBP), microglia & macrophages (Iba1), astrocytes (GFAP), and T lymphocytes (CD3). Digital image analysis of these stained tissues provides quantitative measures of demyelination and inflammation in spinal cord.
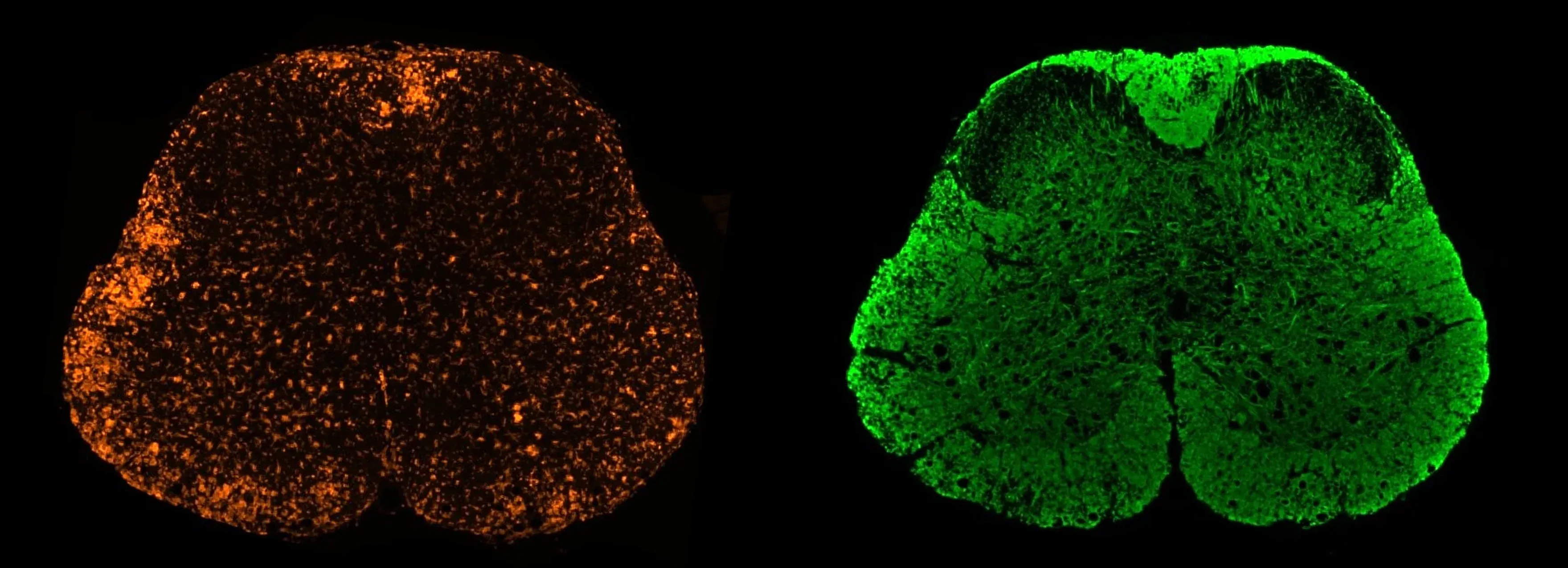
Multiplex immunofluorescence images of microglia (left) and myelin (right) in the spinal cord of MOG35-55 EAE mice.
These endpoints span multiple domains – clinical, biochemical, and histological – providing complementary measures of disease severity and therapeutic impact. Notably, the inclusion of translational biomarkers, such as NfL concentrations, helps bridge preclinical findings to the clinic. Neurofilament light (NfL) is a well-established marker of neurodegeneration & axonal damage: when neurons/axons are damaged, NfL is released into CSF and blood. In clinical studies, elevated NfL levels correlate with disease progression in various neurological disorders, including MS. In our EAE model studies, we observe a similar pattern – as neurons & axons degenerate, CSF & plasma NfL levels increase. This mirrored trend underscores the predictive, translational value of our readouts. By tracking such biomarkers longitudinally in vivo, we can quantitatively monitor disease progression and detect therapeutic effects in a way that is directly relatable to patient outcomes.
In addition to these outcome measures, Biospective distinguishes itself by offering seamless end-to-end integration of all study components. We handle every aspect of the experiment – from model induction, longitudinal behavioral testing, biofluid collection/analysis, and post-mortem tissue analysis. Our scientific team employs advanced analytics (including automated image analysis for demyelination & inflammation and AI-driven cell morphology classification) to extract rich datasets from the model. All data are rigorously analyzed and integrated into an interpretable report, allowing you to make informed decisions on your therapeutic candidate’s performance.
Biospective's EAE Model Expertise and Services
Biospective is a global neuroscience CRO with deep expertise in MS animal models, including the EAE model, which is a core part of our service portfolio.
Our team has over 15 years of experience executing studies in EAE models. We bring our scientific and operational expertise to provide high-quality studies to our sponsors seeking to outsource their in vivo research.
Some key advantages of partnering with Biospective for EAE model studies studies include:
-
Extensive Experience & Model Characterization: We have extensively characterized the EAE mouse model through numerous studies over many years, generating datasets that inform best practices and enhance reproducibility. This track record underscores our unique expertise with this MS model.
-
End-to-End Preclinical Services: Biospective provides integrated services from study design through execution and data analysis. Our capabilities include comprehensive in-life assessments (behavioral testing, motor function assays, etc.), neuroimaging (MRI, PET, SPECT, CT), bioanalysis (fluid biomarkers), IHC & multiplex immunofluorescence), and expert data interpretation. This one-stop approach ensures consistency and accelerates timelines.
-
Translational Biomarkers & Readouts: We incorporate translational endpoints that bridge preclinical findings to clinical outcomes. For example, we measure neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels in plasma and CSF as a biomarker of axonal injury in this model, analogous to what is seen in patients. These biomarkers enhance the translatability of study results to human trials.
-
Global Collaboration & Flexibility: We are a global preclinical neuroscience CRO serving biotech and pharmaceutical clients worldwide. Our scientists collaborate closely with sponsors to tailor studies to specific therapeutic mechanisms or targets. We can accommodate custom endpoints or novel treatment paradigms. We also offer flexibility in study design to meet your program’s needs. Importantly, we prioritize scientific rigor, reproducibility, and open communication throughout the partnership.
By leveraging these strengths, Biospective enables biotech and pharma teams to generate decision-quality data in the EAE mouse model efficiently. We pride ourselves on fast project initiation, clear data reporting, and supporting our clients across the preclinical phases of drug development.
Leverage Biospective's EAE Models for MS Drug Development
By partnering with Biospective for your MS research, you gain access to an internationally recognized team of neurobiology experts and a deeply characterized preclinical model that can accelerate your drug development pipeline.
We have extensive experience executing studies in the EAE mouse model – from exploratory proof-of-concept efficacy studies to detailed mechanistic investigations – across a range of therapeutic modalities (small molecules, biologics, antibodies, gene therapies, antisense oligonucleotides, etc.). Our commitment to scientific rigor and translational relevance is reflected in the quality of our data and our continuous innovation in model validation. As a full-service CRO, we integrate study design, execution, analysis, and reporting, ensuring that your MS therapeutic candidates are evaluated with the highest level of expertise and care.
Contact us to learn more about our characterization of the EAE mouse model, our validated measures, and our Preclinical Neuroscience CRO services.
Discover more about our Multiple Sclerosis Models
Related Content
Up-to-date information on Multiple Sclerosis and best practices related to the evaluation of therapeutic agents in MS animal models.
What is EAE (Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis)?
An overview of EAE animal models of multiple sclerosis (MS), including pathophysiology and utilization of positive controls for preclinical therapeutic studies.
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) & Axonal Injury
This resource describes the methods available for measuring axonal damage & axon degeneration, including tissue markers and plasma & CSF neurofilament light chain (NfL; NF-L) levels, in the EAE model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
Demyelination & Remyelination in the Cuprizone Model
An overview of the methods available to measure myelin and oligodendrocytes in the cuprizone demyelination mouse model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
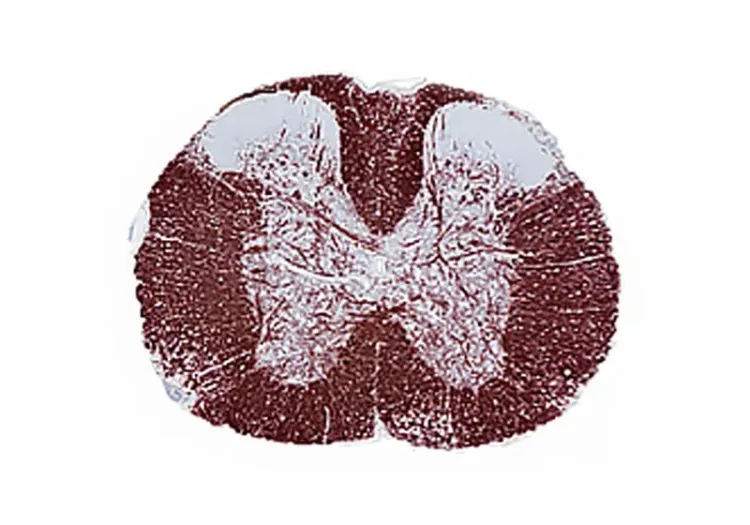
What Is IL-1β (IL-1b)? Function, Signaling, and Biological Role
An overview of IL-1β, including its signaling pathways, involvement in disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets.
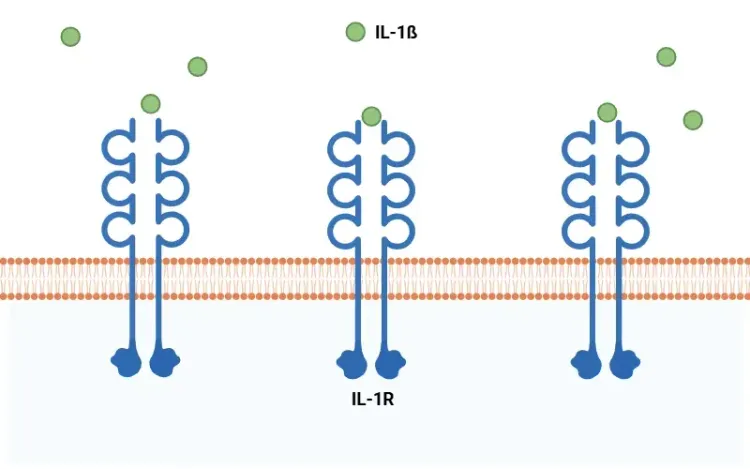
What is NLRP3?
An overview of NLRP3 inflammasome activation triggers, disease associations, and therapeutic targeting strategies.
Autophagy and Transcription Factor EB (TFEB)
An overview of Transcription Factor EB (TFEB) and its role in autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases.
TMEM119 (transmembrane protein 119) and Microglia
An overview of the significance of TMEM119 in labeling microglia and its role in various diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Lysosome Dysfunction in Microglia & Astrocytes
An overview of lysosomal dysfunction in microglia & astrocytes, and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.
What is NF-κB (Nuclear Factor Kappa B)?
An overview of NF-κB, highlighting its role in inflammation and diseases (including neurological disorders), and therapeutic strategies targeting NF-κB.