Biospective’s tau PFF mouse model accelerates neurodegenerative disease drug development with translational tauopathy for preclinical research. As a global neuroscience CRO with expertise in tau PFFs injection into transgenic P301S (PS19) mice, we offer end-to-end in vivo services — including therapeutic efficacy, PK/PD, mechanism-of-action, and target engagement — supported by advanced imaging, quantitative IHC/IF, and clinically relevant biomarkers for biotech and pharma sponsors worldwide.
Overview of the Tau PFF Mouse Model
A disease-relevant tau mouse model for neurodegenerative disease preclinical drug development.
Biological Rationale and Disease Relevance
Tau aggregation and spread are key pathologic features of numerous neurodegenerative diseases, including frontotemporal dementia (FTD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), and Alzheimer's disease. In Biospective’s tau PFF mouse models, tauopathy is induced via the stereotaxic injection of recombinant human tau preformed fibrils into the brains of P301S tau transgenic mice (PS19 line). These fibrils seed endogenous tau misfolding and propagation through anatomically connected regions, recapitulating key features of human tauopathies, including neurofibrillary tangle-like pathology, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration.
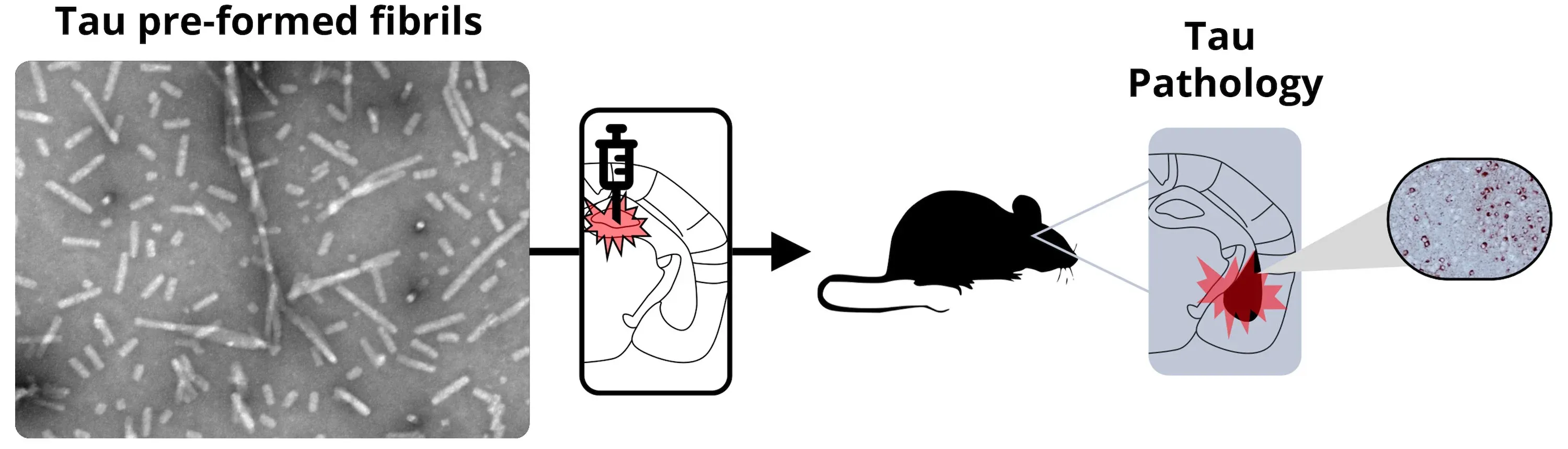
Illustration of unilateral stereotaxic injection of tau PFFs into the mouse hippocampus resulting in seeding and spreading of pathology to anatomically connected brain regions, such as the entorhinal cortex.
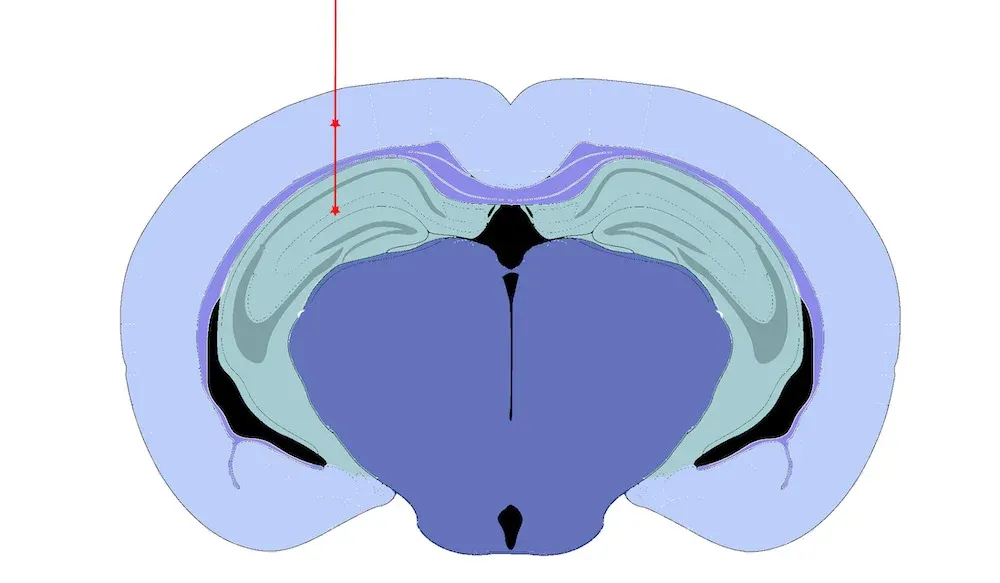
Hippocampus & overlying cortex injection sites.
Validated PFF Injection Sites and Disease Induction
Our validated stereotaxic PFF injection site:
-
Hippocampus ± Cerebral Cortex – targeting pathways involved in multiple tauopathies
For this mouse model, we perform stereotaxic inoculation of preformed fibrils (PFFs) into the hippocampus and overlying cerebral cortex of PS19 transgenic mice [B6;C3-Tg(Prnp-MAPT*P301S)PS19Vle/J]. These transgenic mice overexpress human tau with P301S mutation. The injection site was originally reported by Iba et al., J. Neurosci., 33: 1024-1037.
All injections are performed by our expert team using digital stereotaxic devices with automated microinjectors for highly accurate and precise delivery of sonicated tau PFFs to the target region. A distinct advantage of our tau PFF model is acceleration of pathology compared to conventional transgenic models. We typically perform PFF injections into 8 week-old mice, thereby dramatically reducing study timelines.
We can also use human brain extracts/homogenates as a substitute for the recombinant fibrils in this mouse model.
Key Disease Features and Redouts of the Tau PFF Model
Biospective’s tau PFF mouse model faithfully recapitulates many hallmarks of tauopathy with clinically aligned endpoints for efficacy and target engagement studies.
Notable translational features observed in this model include:
-
Misfolded tau aggregation and spread: Abundant phosphorylated tau inclusions (neurofibrillary tangle–like aggregates) develop and propagate in a stereotypical spatiotemporal pattern throughout connected brain regions. Pathology initiated at a focal injection site gradually appears in downstream regions (reflecting the prion-like spread of tau). The induction of pathology is highly penetrant (~100% of PFF-injected mice) and reproducible in its distribution.
-
Robust Neuroinflammation: The model elicits activation of astrocytes and microglia in regions accumulating tau aggregates. This neuroinflammation (microgliosis, astrogliosis) parallels that seen in human brains, providing an opportunity to evaluate anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory interventions. (See our Resource: Microglia, Astrocytes & Tau in Neurodegenerative Diseases)
- Neurodegeneration: Progressive loss of neurons and degeneration of their processes is a key outcome. This neurodegeneration is accompanied by surrogate biomarkers – for example, we observe elevated neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels in the plasma and CSF of tau PFF-seeded mice.
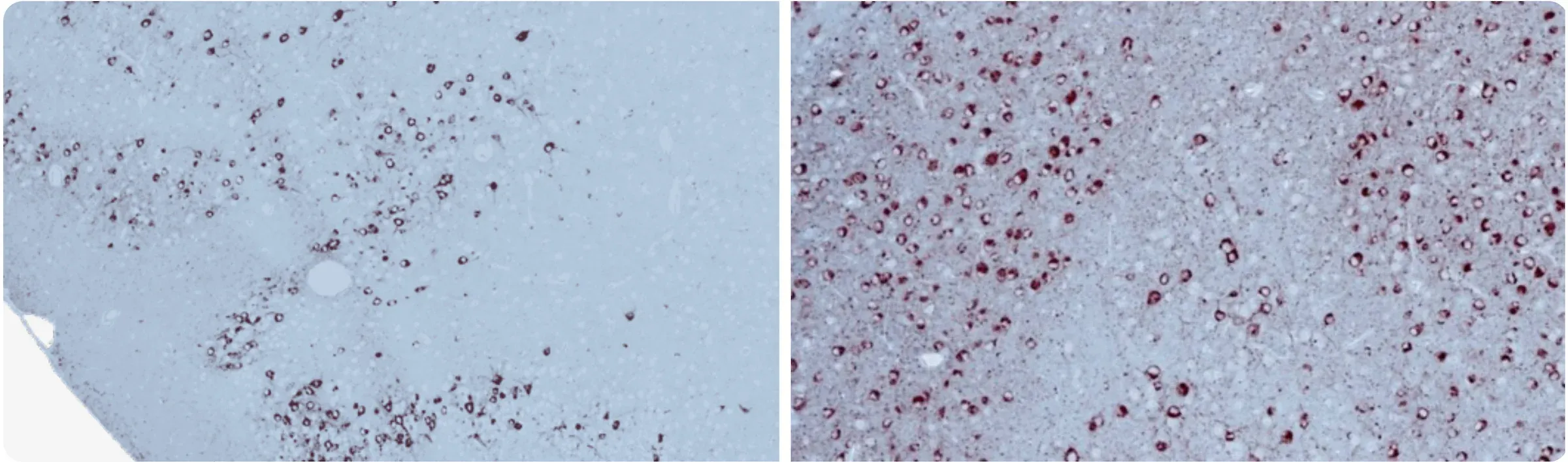
AT8 tau immunohistochemistry staining & brightfield imaging at 12 weeks following stereotaxic injection of recombinant tau preformed fibrils.
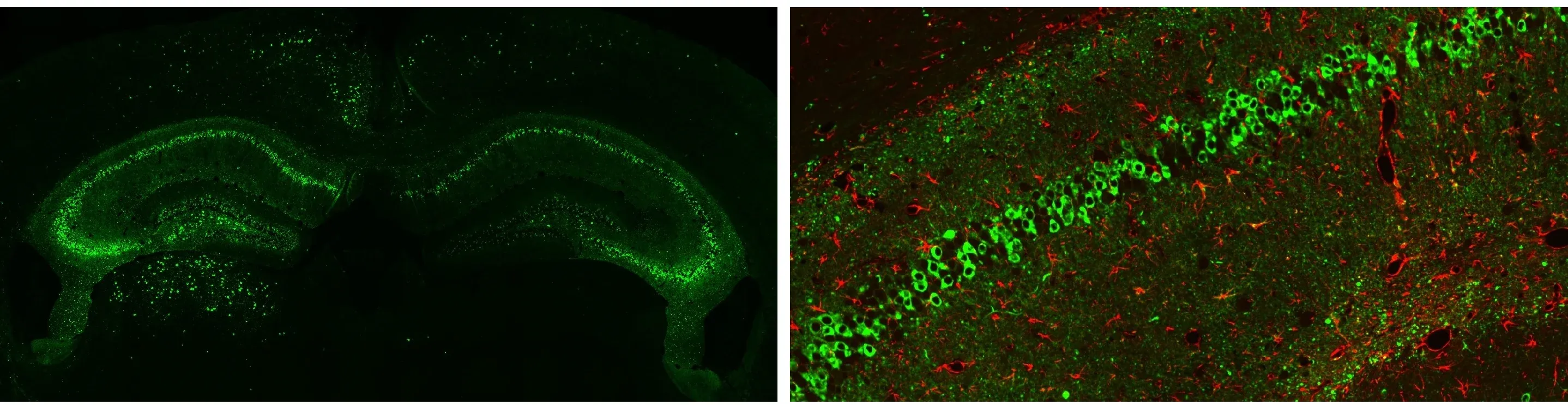
Phosphorylated Tau (AT8 staining; green) in the ipsilateral (left) hemisphere and contralateral (right) hemisphere of Tau PFF-injected PS19 mice, as well as high magnification multiplex immunofluorescence image showing the associated astrogliosis (red).
Accelerating Tau Therapeutic Testing
Biospective’s tau PFF mouse models is well-suited for efficacy testing, mechanism-of-action investigations, and target engagement evaluation of new tau-targeted disease-modifying therapies.
We have successfully employed this neurodegenerative disease model to test a wide range of therapeutic modalities, including small molecule neuroprotective compounds, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), gene therapies (e.g. AAV vectors), and antibody or vaccine-based immunotherapies. This model allows us to customize study endpoints to the specific mechanism of action of the therapy being tested. For example, we can assess target engagement by measuring reductions in tau pathology burden or changes in downstream signaling; we can evaluate biodistribution and pharmacodynamics by sampling tissues and fluids at various time points; and we can determine therapeutic efficacy by improvements in IHC/mIF and biomarker profiles relative to controls.
By partnering with Biospective, pharmaceutical and biotech researchers gain access to a thoroughly characterized, translationally relevant tau model and the scientific expertise to utilize it effectively to evaluate putative disease-modifying therapeutics. Biospective offers a unique combination of a well-established tau animal model and deep scientific know-how. Our tau PFF mouse model, coupled with our end-to-end preclinical CRO capabilities, positions us to be a valued preclinical partner in advancing novel tau-targeted therapies for neurodegenerative diseases.
Contact us to learn more about our characterization of this Tau PFF mouse model, our validated measures, and our Preclinical Neuroscience CRO services.
Discover more of our Tauopathies Models
Related Content
Up-to-date information on Tau and best practices related to the evaluation of therapeutic agents in tauopathy animal models.
PS19 Mouse Model for Tau Targeted Drug Development
An overview of PS19 (P301S) mice as a transgenic model for preclinical evaluation of disease-modifying therapies targeting tau seeding & spreading.
A Guide to Mouse Models of Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
A Resource providing a comprehensive overview of animal models used in frontotemporal dementia research, including genetic and pathological disease mechanisms.
Microglia, Astrocytes & Tau in Neurodegenerative Diseases
How glial-driven neuroinflammation fuels tau aggregation, propagation, and neuronal loss in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies.
Autophagy & Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of how cellular autophagy plays a role in brain health and neurodegeneration.
Lysosome Dysfunction in Microglia & Astrocytes
An overview of lysosomal dysfunction in microglia & astrocytes, and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.
Interleukin-1 Beta (IL-1β) and Neurodegenerative Diseases
The role of IL-1beta in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
TNF-α (TNF-alpha) & Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of the function of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in microglia and its contribution to the progression of neurodegeneration.
Microglial Senescence and Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of microglial senescence and its role in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD).
NLRP3 Inflammasome and Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of the NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson’s disease, and ALS.
What is NF-κB (Nuclear Factor Kappa B)?
An overview of NF-κB, highlighting its role in inflammation and diseases (including neurological disorders), and therapeutic strategies targeting NF-κB.
TNF-α & (TNF-alpha) Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases
An overview of TNF-α signaling in astrocytes, its role in neurodegeneration, and therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway..