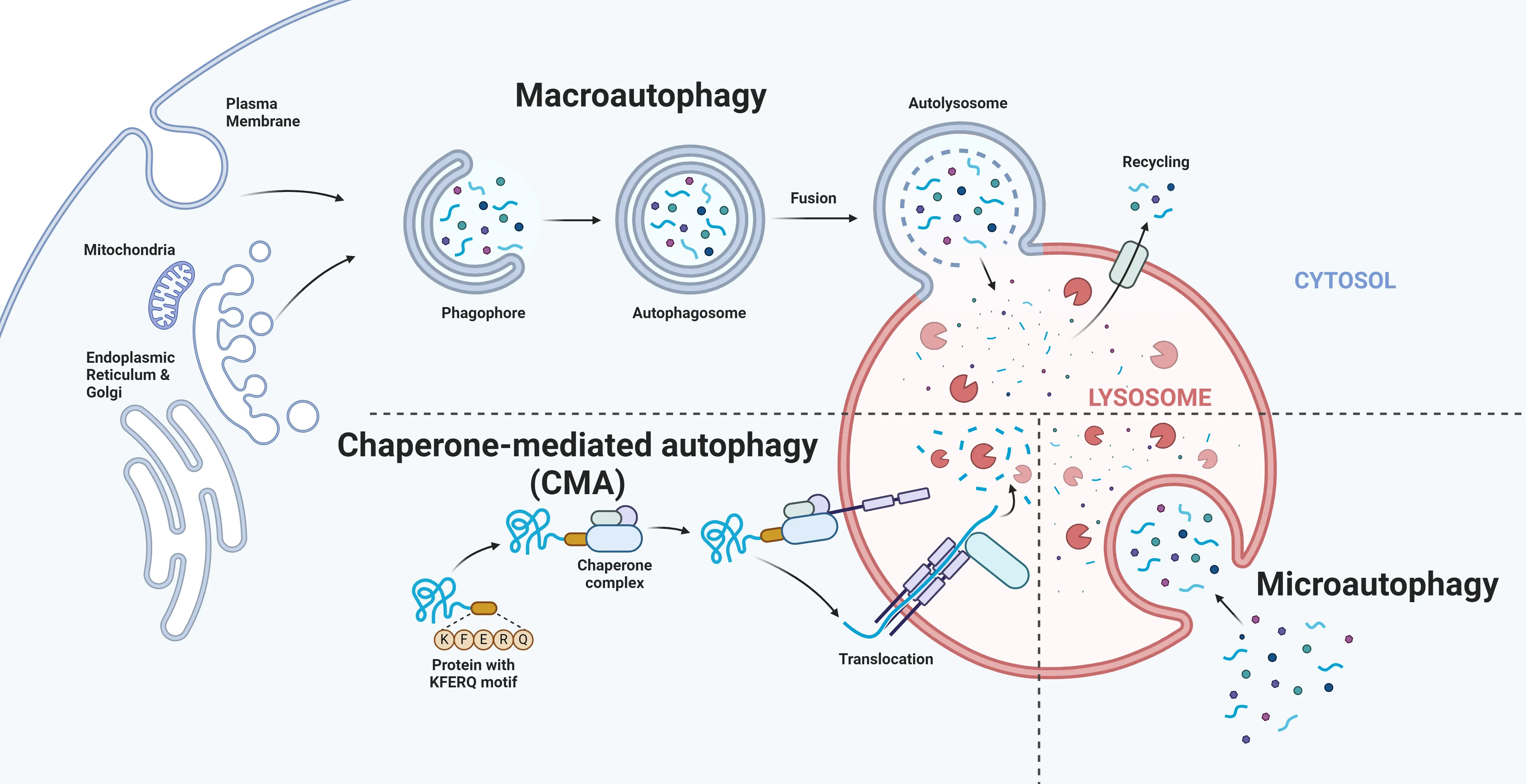
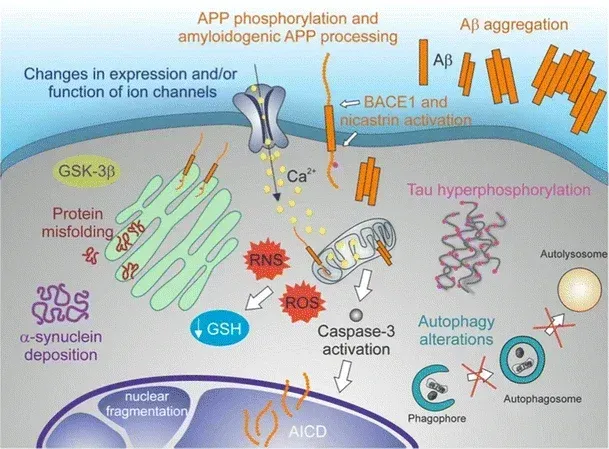
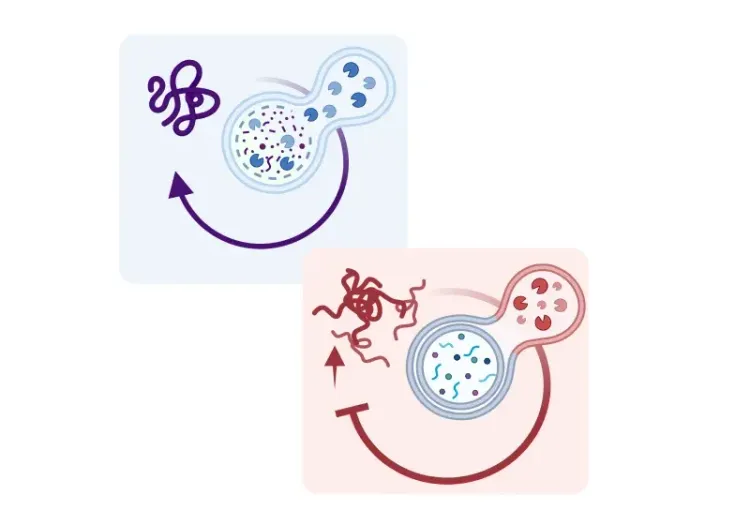
Barmada, S.J., Serio, A., Arjun, A., et al. Autophagy induction enhances TDP43 turnover and survival in neuronal ALS models. Nat. Chem. Biol., 10: 677–685, 2014; doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1563
Bar-Yosef, T., Damri, O., Agam, G. Dual role of autophagy in diseases of the central nervous system. Front. Cell. Neurosci., 13:196, 2019; doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00196
Beilina, A., Cookson, M.R. Genes associated with Parkinson’s disease: Regulation of autophagy and beyond. J. Neurochem., 139: 91–107, 2016; doi: 10.1111/jnc.13266
Bhukel, A., Beuschel, C.B., Maglione, M., et al. Autophagy within the mushroom body protects from synapse aging in a non-cell autonomous manner. Nat. Commun., 10: 1318, 2019; doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09262-2
Caccamo, A., Majumder, S., Richardson, A., et al. Molecular interplay between mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), amyloid-β, and tau: Effects on cognitive impairments. J. Biol. Chem., 285: 13107–13120, 2010; doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.100420
Cai, Q., Ganesan, D. Regulation of neuronal autophagy and the implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis., 162: 105582, 2022; doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105582
Cuervo, A.M., Stefanis, L., Fredenburg, R., et al. Impaired degradation of mutant α-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science, 305: 1292–1295, 2004; doi: 10.1126/science.1101738
De Chiara, G., Marcocci, M.E., Sgarbanti, R., et al. Infectious agents and neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol., 46, 614–638 (2012); doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8320-7
Deng, Z., Purtell, K., Lachance, V., et al. Autophagy receptors and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Cell Biol., 27: 491–504, 2017; doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.01.001
Esteves, A.R., Palma, A.M., Gomes, R., et al. Acetylation as a major determinant to microtubule-dependent autophagy: Relevance to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson disease pathology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis., 1865: 2008–2023, 2019; doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.11.014
Feng, Q., Luo, Y., Zhang, X.-N., et al. MAPT/tau accumulation represses autophagy flux by disrupting IST1-regulated ESCRT-III complex formation: A vicious cycle in Alzheimer neurodegeneration. Autophagy, 16: 641–658, 2020; doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1633862
Frake, R.A., Ricketts, T., Menzies, F.M., Rubinsztein, D.C. Autophagy and neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Invest., 125: 65–74, 2015; doi: 10.1172/JCI73944
Hara, T., Nakamura, K., Matsui, M., et al. Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature, 441: 885–889, 2006; doi: 10.1038/nature04724
Hou, X., Watzlawik, J.O., Fiesel, F.C., Springer, W. Autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Biol., 432: 2651–2672, 2020; doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.037
Kesidou, E., Lagoudaki, R., Touloumi, O., Poulatsidou, K.-N., Simeonidou, C. Autophagy and neurodegenerative disorders. Neural Regen. Res., 8: 2275–2283, 2013a; doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.24.007
Klionsky, D.J., Abdelmohsen, K., Abe, A., et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy, 12: 1–222, 2016; doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356
Lee, J., Giordano, S., Zhang, J. Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: Cross-talk and redox signalling. Biochem. J., 441: 523–540, 2011; doi: 10.1042/BJ20111451
Lee, J.K., Shin, J.H., Lee, J.E., Choi, E.-J. Role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis., 1852: 2517–2524, 2015; doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.08.005
Menzies, F.M., Fleming, A., Caricasole, A., et al. Autophagy and neurodegeneration: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Neuron, 93: 1015–1034, 2017; doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.01.022
Mizushima, N., Yamamoto, A., Matsui, M., et al. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol. Biol. Cell, 15: 1101–1111, 2004; doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-09-0704
Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T. How to interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy, 3: 542–545, 2007; doi: 10.4161/auto.4600
Nah, J., Yuan, J., Jung, Y.-K. Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: From mechanism to therapeutic approach. Mol. Cells, 38: 381–389, 2015; doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0034
Nakatogawa, H., Suzuki, K., Kamada, Y., Ohsumi, Y. Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: Lessons from yeast. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 10: 458–467, 2009; doi: 10.1038/nrm2708
Nilsson, P., Loganathan, K., Sekiguchi, M., et al. Aβ secretion and plaque formation depend on autophagy. Cell Rep., 5: 61–69, 2013; doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.08.042
Nixon, R.A. Autophagy in neurodegenerative disease: Friend, foe or turncoat? Trends Neurosci., 29: 528–535, 2006; doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2006.07.003
Nixon, R.A. Autophagy, amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer disease. J. Cell Sci., 120: 4081–4091, 2007; doi: 10.1242/jcs.019265
Nixon, R.A. The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Med., 19: 983–997, 2013; doi: 10.1038/nm.3232
Orenstein, S.J., Kuo, S.-H., Tasset, I., et al. Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat. Neurosci., 16: 394–406, 2013; doi: 10.1038/nn.3350
Pickford, F., Masliah, E., Britschgi, M., et al. The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid β accumulation in mice. J. Clin. Invest., 118: 2190–2199, 2008; doi: 10.1172/JCI33585
Rudnick, N.D., Griffey, C.J., Guarnieri, P., et al. Distinct roles for motor neuron autophagy early and late in the SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 114: E8294–E8303, 2017; doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704294114
Shibata, M., Lu, T., Furuya, T., Degterev, A., Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T., MacDonald, M., Yankner, B., & Yuan, J. Regulation of intracellular accumulation of mutant Huntingtin by Beclin 1. J. Biol. Chem., 281:14474–14485, 2006; doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600364200
Son, J.H., Shim, J.H., Kim, K.-H., Ha, J.-Y., & Han, J.Y. Neuronal autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp. Mol. Med., 44: 89–98, 2012; doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.2.031
Spencer, B., Potkar, R., Trejo, M., Rockenstein, E., Patrick, C., Gindi, R., Adame, A., Wyss-Coray, T., & Masliah, E. Beclin 1 gene transfer activates autophagy and ameliorates the neurodegenerative pathology in α-synuclein models of Parkinson’s and Lewy body diseases. J. Neurosci., 29: 13578–13588, 2009; doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4390-09.2009
Stavoe, A.K.H., & Holzbaur, E.L.F. Autophagy in neurons. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 35: 477–500, 2019a; doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100818-125242
Su, P., Zhang, J., Wang, D., Zhao, F., Cao, Z., Aschner, M., & Luo, W. The role of autophagy in modulation of neuroinflammation in microglia. Neuroscience, 319: 155–167, 2016; doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.01.035
Vidal, R.L., Matus, S., Bargsted, L., & Hetz, C. Targeting autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 35: 583–591, 2014; doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2014.09.002
Vogiatzi, T., Xilouri, M., Vekrellis, K., & Stefanis, L. Wild type α-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J. Biol. Chem., 283: 23542–23556, 2008; doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801992200
Williams, A., Jahreiss, L., Sarkar, S., Saiki, S., Menzies, F.M., Ravikumar, B., & Rubinsztein, D.C. Aggregate-prone proteins are cleared from the cytosol by autophagy: Therapeutic implications. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol., 76: 89–101, 2006; doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(06)76003-3
Wu, J., Qi, L., Wang, Y., Kegel, K.B., Yoder, J., Difiglia, M., Qin, Z., & Lin, F. The regulation of N-terminal Huntingtin (Htt552) accumulation by Beclin1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 33: 743–751, 2012; doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.14
Yang, Z., & Klionsky, D.J. Mammalian autophagy: Core molecular machinery and signaling regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 22: 124–131, 2010; doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.014
Zhang, C., Chen, S., Li, X., Xu, Q., Lin, Y., Lin, F., Yuan, M., Zi, Y., & Cai, J. Progress in Parkinson’s disease animal models of genetic defects: Characteristics and application. Biomed. Pharmacother., 155: 113768, 2022; doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113768
Zhang, L., Yu, J., Pan, H., Hu, P., Hao, Y., Cai, W., Zhu, H., Yu, A.D., Xie, X., Ma, D., & Yuan, J. Small molecule regulators of autophagy identified by an image-based high-throughput screen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 104: 19023–19028, 2007; doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709695104