Tau Model Overview
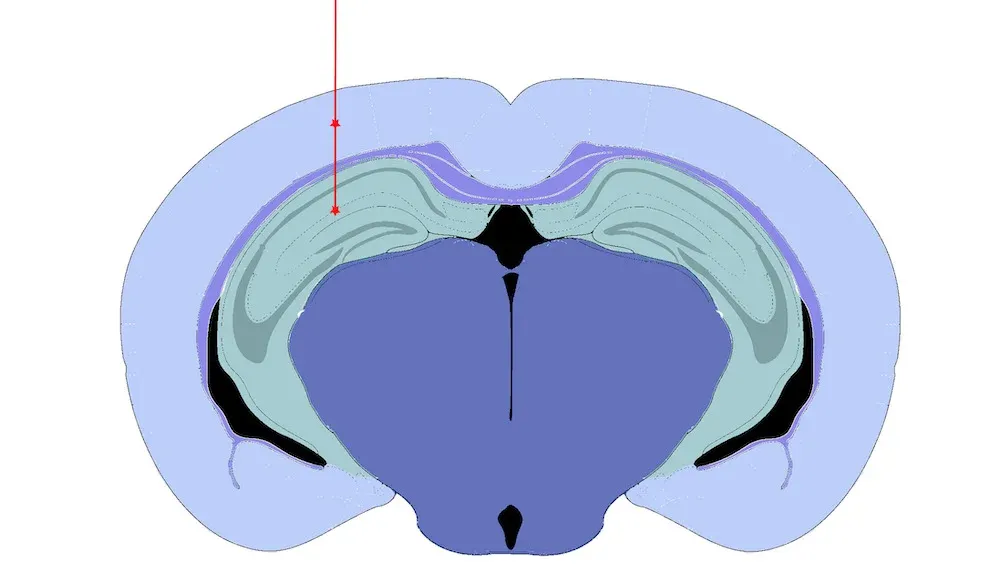
For this Alzheimer's disease model, we perform stereotaxic inoculation of preformed fibrils (PFFs) into the hippocampus and overlying cerebral cortex of PS19 transgenic mice [B6;C3-Tg(Prnp-MAPT*P301S)PS19Vle/J]. These transgenic mice overexpress human tau with P301S mutation. The injection site was originally reported by Iba et al., J. Neurosci., 33: 1024-1037, 2013; doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2642-12.2013).
Tau Model Generation
A general schema for tau PFF animal model generation is:
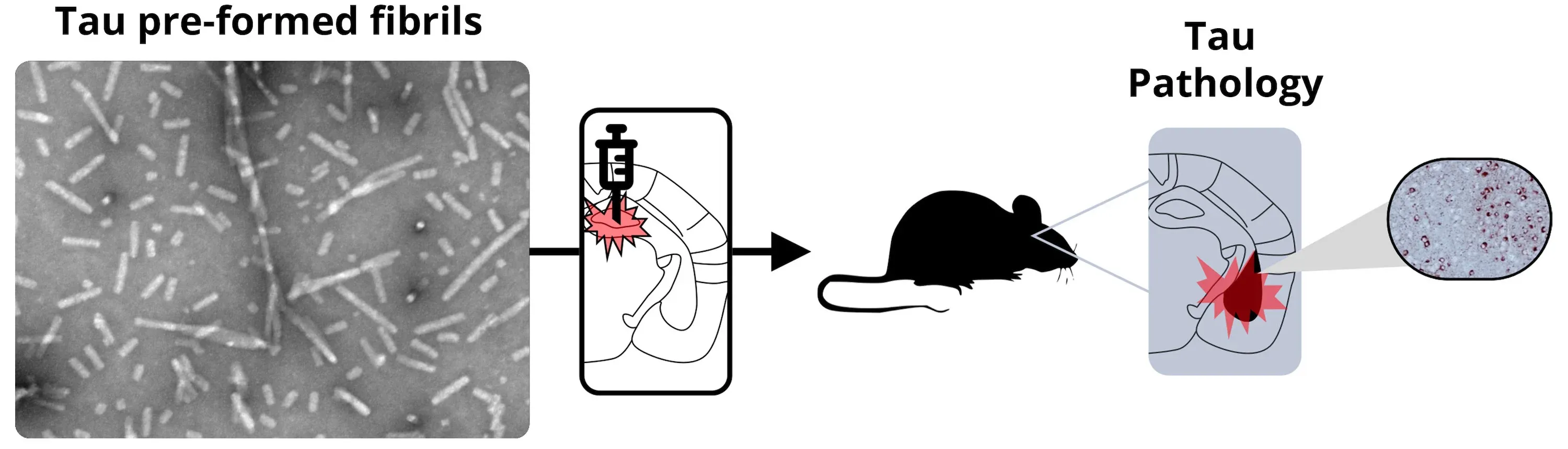
We can also use human brain extracts/homogenates as a substitute for the recombinant fibrils in this model.
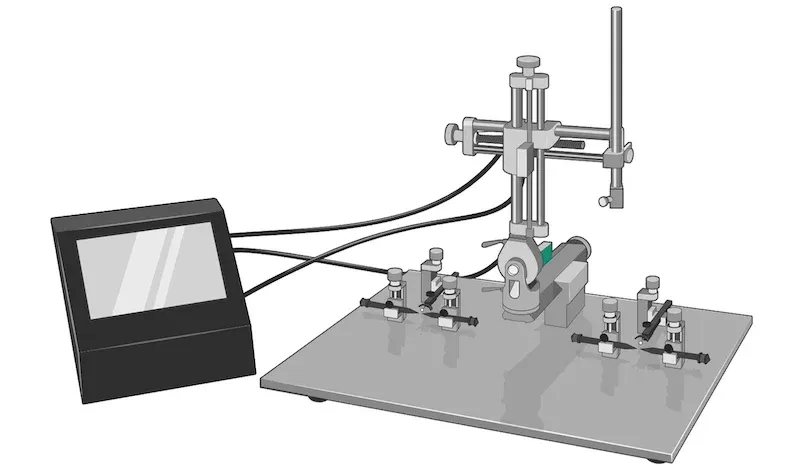
For this specific mouse model, we use PS19 male mice at 8 weeks-of-age. We then perform stereotaxic injection of sonicated, recombinant human tau PFFs or brain extracts into the hippocampus and overlying cortex.
We use digital stereotaxic devices with automated microinjectors for high accuracy & precision.
This animal model is highly reproducible with a nearly 100% success rate of tau PFF seeding.
Our Tau Mouse Model Validated Measures
- Body weight
- Clinical scores
- Neurofilament Light measures in plasma & CSF
- Immunohistochemistry & multiplex immunofluorescence
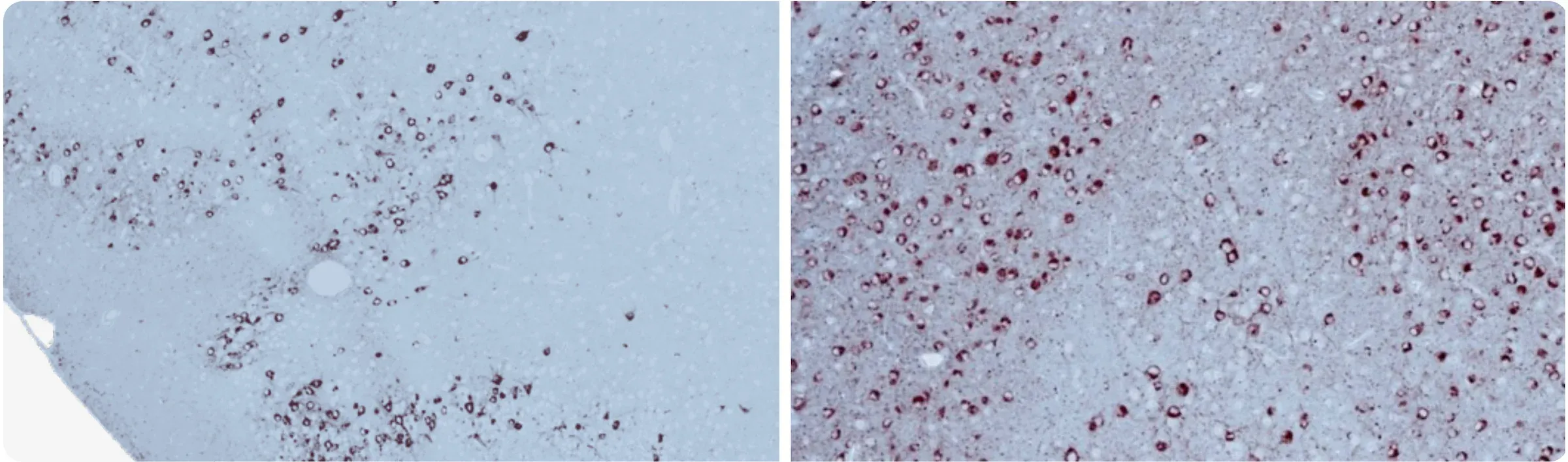
AT8 tau immunohistochemistry staining at 12 weeks following stereotaxic injection of recombinant tau preformed fibrils.
Learn more about our characterization of this model, our validated measures, and our Preclinical Neuroscience CRO services.